What is a Limit Order in Stocks? Beginner’s Guide

Trading stocks can be exciting and profitable because of the potential for a security’s value to rise due to volatility. However, like other investments, stock trading can result in losses if the market conditions are unfavorable.
One of the most effective ways seasoned stock investors and traders manage the risk of losing money is through a limit order. Brokers offer the trading feature to allow traders to control the price limits they wish to buy or sell a security. What is a limit order in stocks? How can traders use it to execute trades? We answer these questions and more in this guide.
-
-
Definition and Purpose of Limit Orders
Whether you are a beginner or a pro trader, you must have heard or read about different order types on the best stock trading apps. These include market, stop, and limit orders. Many beginner traders commonly use limit orders because they offer better control.
Your capital is at risk.
What is a Limit Order in Stocks?
A limit order in stock trading or any other financial market is an instruction from a trader to a broker to buy or sell a security at a specific price. The trader usually determines the price they consider right for the trading platform to acquire or let go of the asset. They also determine how long the order should stay open before it is filled or expires.
The order period ranges from one broker to another and aligns with traders’ preferences. A day trader can set a buy or sell order on the best day trading apps to control the best price they prefer to buy or sell stock shares.
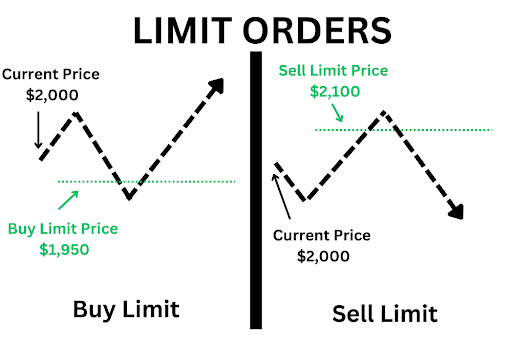
In other words, traders can place a limit order as a buy or sell order. With a buy limit order, you instruct a stock investment app to purchase stocks at a particular price (the limit price) or a lower value. Conversely, you instruct a broker to sell a security at a specific price or a higher value using a sell limit order.
Note that both order types are time-bound. That means the order expires if the broker cannot fill it within the stipulated period. In a situation where it expires, you have your money in your trading balance to place another order on the next trading day or in the future.
For instance, you want to sell 100 shares of a stock at $10 per share. However, after a detailed market analysis, you believe the asset’s price can rise to $15 in a few days. You can open a sell limit order to trade the shares at $13 or higher within a week or two.
Your broker won’t sell the security until it rises to $13 per share within the stipulated period. If the price reaches that value, the broker fills the order. Otherwise, it automatically expires, and it won’t sell your shares.
The same logic applies to a buy limit order, which instructs a broker to purchase a security at a specific or lower price during a preset period. For instance, you can instruct a penny stock app to buy low-value shares when their prices fall to or below a specific price. If the asset doesn’t meet the preset price, you can cancel the order or leave it to expire automatically.
However, it’s important to note that limit orders are not limited to only stock trading. Cryptocurrency investors can also set limit orders on various crypto trading apps to determine buying or selling prices for Bitcoin, Ethereum, and a diverse range of altcoins.
How Limit Orders Differ from Market Orders
As stated earlier, traders use different order types to manage risks and minimize losses. Though buy and sell limit orders are popular, investors also leverage market orders to minimize losses during trades.
Combining different order types can help develop an effective stock trading strategy. So, apart from understanding “What is a limit order in stocks?”, knowing what market order is is essential.
Limit orders allow traders to determine an asset’s buying or selling price over a specific period. On the other hand, a market order allows you to buy or sell a stock at the market’s best available price. In other words, a limit order can be used for instant and future trades, while a market order is for instant trade execution only.
Market orders execute trades immediately as stock prices rise and fall, hoping to profit from price increases from the next available price. So, with a market order, you can instantly execute trades regardless of a stock’s price. But for a limit order, you have a specific price for trade execution.
However, unlike limit orders with a guaranteed buying or selling price, the risk with market orders is that there are no price guarantees. The broker fills your order based on current market realities, and the best price during the trading period may be unfavorable.
In other words, a limit order primarily deals with an asset’s price and will not execute a transaction until its value meets the trader’s expectations. Conversely, a market order primarily deals with timely order execution. So, it prioritizes transaction speed over price.
The best way to navigate the various order types is to thoroughly understand their working mechanisms and how to infuse them into your strategy to save money. You can decide which order type is best at a particular time after conducting detailed research using the best stock analysis apps.
These order types are also available to investors in other financial markets. For example, forex traders can execute trades on top forex apps using a limit, stop, or market order.
Order Type Trade Execution Limit Order Buys or sells a security at a specific price over a stipulated period Market Order Instantly purchases or sells a stock at the best market price during a trading window Your capital is at risk.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Limit Orders
A limit order is an efficient tool that can help mitigate the risk of losses during trades. Traders can use a limit order when a stock’s price is rising and falling quickly to avoid a bad fill from market orders. However, limit orders are not devoid of risks.
Below, we highlight the pros and cons of using limit orders in stocks.
Pros:
- A limit order eliminates emotions from trading. Since the stock market is highly volatile, worrying about entering and closing trades at the wrong time is normal. However, traders can manage their emotions better by setting a limit order to execute buy and sell orders at the best prices.
- A limit order saves time committed to active trading. Active traders often need to monitor trades on stock portfolio trackers for long hours to place multiple orders. A limit order can reduce the time active traders spend buying and selling stocks. You only need to set a limit order and leave your broker to execute trades accordingly.
- Limit orders make better profits. The goal of trading stocks is to lock in significant gains. Limit orders can help make huge returns with fewer risks. With the order type, you can buy or sell a stock at the best possible price, depending on your projections. Your order will not go through if the asset’s price doesn’t reach the predicted value.
- You can manage multiple shares with a limit order. If you trade many shares simultaneously, limit orders can help combine and trade them efficiently. Doing so will help you avoid slippage, even when you cannot monitor all the trades simultaneously.
- Limit orders are more suitable for low-volume stocks. Usually, stocks with low market cap and trading volume are more volatile. They also take longer to execute transactions using market orders. You can leverage limit orders to manage risks and trade at your preferred price. This helps avoid paying too much for an asset or selling at a significantly lower cost.
Cons:
- There are no guarantees of trade execution. Your order may not go through when using limit orders for trade execution. This is because you have a specific price that the stock may fail to meet during the set period.
- Longer execution time. Unlike market orders, limit orders usually take longer to execute trades. The delay happens because the order type waits for market conditions that align with a trader’s price expectations.
- Potential missed opportunities. Trading with limit orders can result in missing out on the opportunity to make better gains from market price movements. This happens when an asset quickly rises or falls, and your proposed price is lower (for selling) or higher (for buying).
Types of Limit Orders
Infusing limit orders into your trades requires understanding the different limit order types and how they work. We highlight the common types of limit orders below.
Limit Buy Orders
What is a buy limit order? A buy limit or limit buy order instructs a broker to purchase an asset at a specific price or a lower amount. With a buy limit order, a trader can buy stock shares at a guaranteed price or less.
For instance, a Tesla (TSLA) share costs about $240 at the time of writing. If you anticipate a price fall, you can use a buy limit order to purchase the shares at $220 per share or less over the next 30 days. If the asset’s price doesn’t meet your asking price, the transaction will not happen. In other words, your order will not be filled.
However, while the potential buying price is certain, there are no guarantees that the stock’s price will reach the price you specified. That means you can miss out on trading opportunities unless you set a market order for immediate trade execution at the best market price.
Alternatively, you can set a stop limit order to execute the trade once the stock price reaches a specific stop price, especially if it increases.
The advantage of a buy limit order is ensuring you don’t purchase an asset at a lower price than expected. Thereby preventing more potential losses due to continuous price falls.
Limit Sell Orders
A limit sell order or sell limit order is the opposite of a limit buy order. The order type allows you to sell a stock at a specific price or a higher value within a trading window. The goal is to sell your asset at a projected price, which is usually higher than its current value.
Like limit buy orders, there’s no assurance that the stock value will reach your proposed selling price. You are only aiming to trade it at $260 or more. So, if it doesn’t reach your limit price, inform your broker at the end of the set trading period not to execute the trade.
Order Type Trade Execution Buy Limit Order Automatically purchases a stock at a specific price or lower value during a defined period Sell Limit Order Sells a stock at a predetermined price or better during a specific period Conditional and Contingent Limit Orders
Since there’s the possibility that a stock’s value may rise or fall above or below a specified limit price, brokers allow traders to combine two or more order types into one order. These order types are conditional and contingency limit orders.
Conditional and contingency orders are often used interchangeably but differ slightly.
A conditional limit order is an advanced order instructing a broker to execute orders based on preset conditions that an asset must meet. The order can be a limit, stop, or stop limit order.
For instance, if a stock trades at $50 per share, you can set a buy limit order to purchase it at $45 before the trading day ends. That means the order has two conditions. The first is to buy the asset at $45 or lower, and the other is to execute or cancel the order within a trading day.
A contingent order is a variant of conditional limit orders that allows you to execute two trades simultaneously. This order type is ideal for investors trading many shares. It allows them to complete two or more conditional transactions.
In other words, a contingent order allows a broker to execute a secondary transaction if an asset doesn’t meet the trader’s primary conditions. For instance, a contingent limit order can instruct a broker to buy or sell another stock if an S&P 500 asset’s value falls below a specific price.
Order Type Trade Execution Conditional Order Automatically buys or sells a stock based on preconfigured conditions from any order type Contingent Order Executes two or more trades simultaneously using different market conditions How Limit Prices Are Set
Determining the Optimal Limit Price
When setting a limit price, the first thing is to determine the best price you want to buy or sell a stock. Usually, the price-determining process requires adequate research to accurately predict the rise or fall in an asset’s future value.
In other words, getting the optimal limit price for an asset requires fundamental and technical analyses. You can use any of our recommended stock market research and analysis software to determine stock performance and make informed decisions.
Considering Market Conditions and Trends
Market trends are another factor to consider when setting limit prices for your orders. Like other speculative investments, market conditions and trends usually impact stock prices. So, before setting your price limit, get market insights from stock tips service providers and assess current market conditions.
Doing so will help you find the best bid or ask price for the stock you want to trade.
Impact of Bid-Ask Spread on Limit Prices
A bid-ask spread measures an asset’s demand and supply. The bid represents the demand for a stock, and the ask represents its supply. When setting a limit price, consider the stock’s tokenomics and bid-ask spread, which is the gap between its demand and supply. The spread helps determine if a broker will execute a limit order successfully.
A wide big-ask spread means fewer people are interested in buying a stock, making it harder and longer to fill orders. That way, you’ll pay more fees as a buyer or receive lesser value as a seller.
Conversely, a tight spread indicates significant demand for the asset, resulting in quicker order fills, lower fees, and better returns.
Time-in-Force (TIF) Options for Limit Orders
Many active traders use time-in-force (TIF) to limit the active periods of a limit order. Since such traders execute many trades, using TIF helps them manage their orders and control how long they stay open.
Now, let’s look at the four most common TIF options you can set for your limit orders.
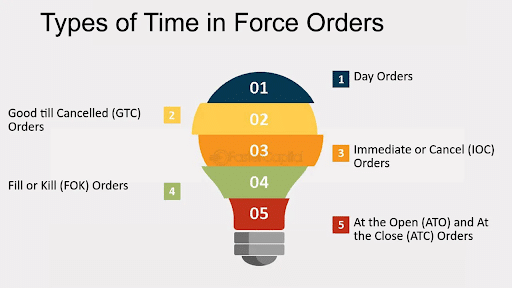
Day Orders vs. Good ’til Canceled (GTC) Orders
As the name implies, day orders are short-term limit orders that a broker must fill before a day’s trading session ends. Failure to do so results in the broker automatically canceling the order.
Good ’til canceled (GTC) orders are long-term limit orders that leave a trade open to be filled until the trader or broker cancels it. Usually, a GTC order lasts for 3 months.
Order Type Trade Execution Day Order Executes a limit order before the end of a trading day or cancels it Good ‘til canceled Order Leaves a limit order open until its conditions are met or the stipulated trading period lapses Immediate or Cancel (IOC) and Fill or Kill (FOK) Orders
An immediate or cancel (IOC) order requires immediate execution. The order type instructs a broker to buy or sell a stock instantly. Any portion of the order that doesn’t get filled instantly is canceled and deleted from the broker’s order book.
However, a fill or kill (FOK) order requires instant and full execution. An FOK order doesn’t offer partial execution. So, the broker cancels the trade if it cannot be completely filled within the stipulated trading period.
Order Type Trade Execution Immediate or Cancel Order Instantly fills an order and can result in partial execution Fill or Kill Order Immediately completes an order with full execution or cancels the trade Choosing the Right TIF for Your Trading Strategy
TIF orders help traders avoid accidental trade execution. However, choosing the perfect TIF order for your trading strategy depends on your investment goals and risk tolerance.
If you are a day trader looking to execute immediate trades, market orders are ideal for you. Limit orders are best for long-term traders looking for better price control. Stop orders and stop-limit orders are suitable for reducing losses.
Your capital is at risk.
Using Limit Orders for Entry and Exit Strategies
Limit orders are effective for determining stock buying and selling prices, making them effective tools for determining the best entry and exit strategies. Learn how to use limit orders under different market conditions below.
Implementing Limit Orders in Bullish Markets
A bullish market is characterized by a consistent increase in stock prices. Under such market conditions, setting a limit order can help rake in significant profits. A sell limit order in a bullish market can help you sell a stock at the highest price. So, you can infuse this into your market entry strategies.
Utilizing Limit Orders in Bearish Markets
In a bearish market, stock prices constantly fall. Using a buy limit order can help you purchase an asset at the lowest price to sell at a higher price in the future. So, traders can use limit orders for market exit strategies.
Setting Stop-Limit Orders for Risk Management
Stop-limit orders are effective risk-management tools investors can use to reduce their losses from bad trading periods. When the market moves against you, setting a stop price can prevent your order from getting filled if the current stock price is too low or high.
Limit Orders in Volatile Markets
There’s a strong possibility of the market moving against you during moments of high volatility. Learn how to navigate such market conditions using limit orders.
Strategies for Limit Orders in High Volatility
During a period of high volatility, your broker may partially execute your trades or leave them completely unexecuted. An effective way to get the best trading outcomes is to add a stop-loos order to the limit order.
Doing so will allow the broker to ignore existing market conditions and automatically sell your trading position if the stock reaches a specific price point.
Adjusting Limit Orders During News Events
Economic news and other prevalent events in your location can impact stock prices. Staying updated with such information can help you determine when to adjust your market positions. For instance, a negative report can cause price falls, so you should modify your buy or sell limit order to match the current realities.
You can also get updated stock trading signals to make informed decisions.
Pitfalls to Avoid in Volatile Conditions
Trading during volatile market conditions can be challenging because of the higher possibility of losses. The pitfalls to avoid when using limit orders in volatile market conditions include:
- Paying high spreads due to high transaction volumes. Wait until the market is more stable, if possible.
- Using market orders to execute trades in fast markets. You may end up with unfavorable prices.
- Trading low-volume and less-liquid stocks. These come with wider spreads and a lower likelihood of order execution.
- Trading without a strategy or an understanding of your risk tolerance.
If you’re a beginner, you can register on a paper trading app to get familiar with using limit orders for trades before trading with real money.
Monitoring and Managing Open Limit Orders
Though you can leave your trading platform to automatically execute trades after setting a limit order, staying on top of things is crucial. How can you manage your open trades after setting limit orders? We highlight some steps below.
Regularly Reviewing and Adjusting Limit Orders
Monitoring and reviewing your open orders is the easiest way to manage your investments. Market conditions constantly change, so adjust your trading positions in line with current market realities. This will help ensure your order is fully filled, and you trade at the best prices.
Setting Realistic Expectations for Limit Order Execution
Trading stocks with limit orders can help buy an asset at the lowest price or sell it at the highest price. Though you have the freedom of choosing the buy or sell limit price, ensure your expectations are realistic. Having an extremely high or low price can leave your order partially executed or completely unfilled.
Using Limit Orders in Conjunction with Other Order Types
Limit orders are efficient trading tools. However, combining them with other order types can help you trade more effectively and manage risks better. You can combine your limit order with a market order for quicker execution or a stop-loss for risk management.
Your capital is at risk.
Common Limit Order Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Trading stocks with limit orders can help you make the most of the market’s price swings. However, avoiding the potential errors of the trading tool is crucial. We highlight some common mistakes below.
Overcoming Slippage Issues with Limit Orders
One of the common ways traders lose money is through slippage. This occurs when a security’s projected trading price is lower than the actual trade execution price. Slippage is common with market orders and happens during periods of high volatility.
An efficient way to avoid slippage issues is by using limit orders to determine your desired trading price. Also, avoid markets with high volatility and low liquidity.
The Importance of Continuous Market Analysis
Overdependence on limit orders is another mistake to avoid. After placing your order, don’t leave your trades unattended. Monitor the markets consistently to adjust your limit prices. This will help reduce the risk of poor performance or losses.
One of the ways to get good market insights is to mirror trades from seasoned investors using a copy trading app.
Learning from Limit Order Execution Challenges
Another way to improve your trading skills and avoid errors is by taking lessons from limit order execution challenges. These include personal and third-party trading issues like understanding why brokers reject limit orders or fail to execute some limit orders. That way, you can avoid such errors and limit losses.
Recap of Key Takeaways
- A limit order fills an order at a specific price or better.
- Limit orders give traders total control of an order’s execution price.
- A lit order does not guarantee a successful trade execution.
- Factors like market volatility, asset liquidity, and order size can impact a limit order.
- A limit order has a specific execution period (ranging from a day) for an order to be filled.
Encouragement for Incorporating Limit Orders in Trading Strategies
Now you have an answer to the question, “What is a limit order in stocks?” A limit order allows you to control the prices to buy or sell a stock with the hope of making profits. Incorporating limit orders into your trading strategies can help you buy a share at the lowest price or sell at the highest price.
Besides the potential profit, limit orders can help you navigate market volatility better, as you don’t lose your investments if the market conditions don’t go your way. Always remember to check a company’s financial records and understand its stock floats before investing in its shares.
Doing so will help you determine its price volatility, investment risks, and potential earnings per share (EPS).
What is a Limit Order in Stocks? – eToro Complete Guide
eToro is one of the best free stock trading brokers for anyone interested in trading stocks. The online brokerage offers traders tools like limit orders, market orders, and stop-loss. Follow the steps below to join eToro and start trading stocks with your preferred order types.
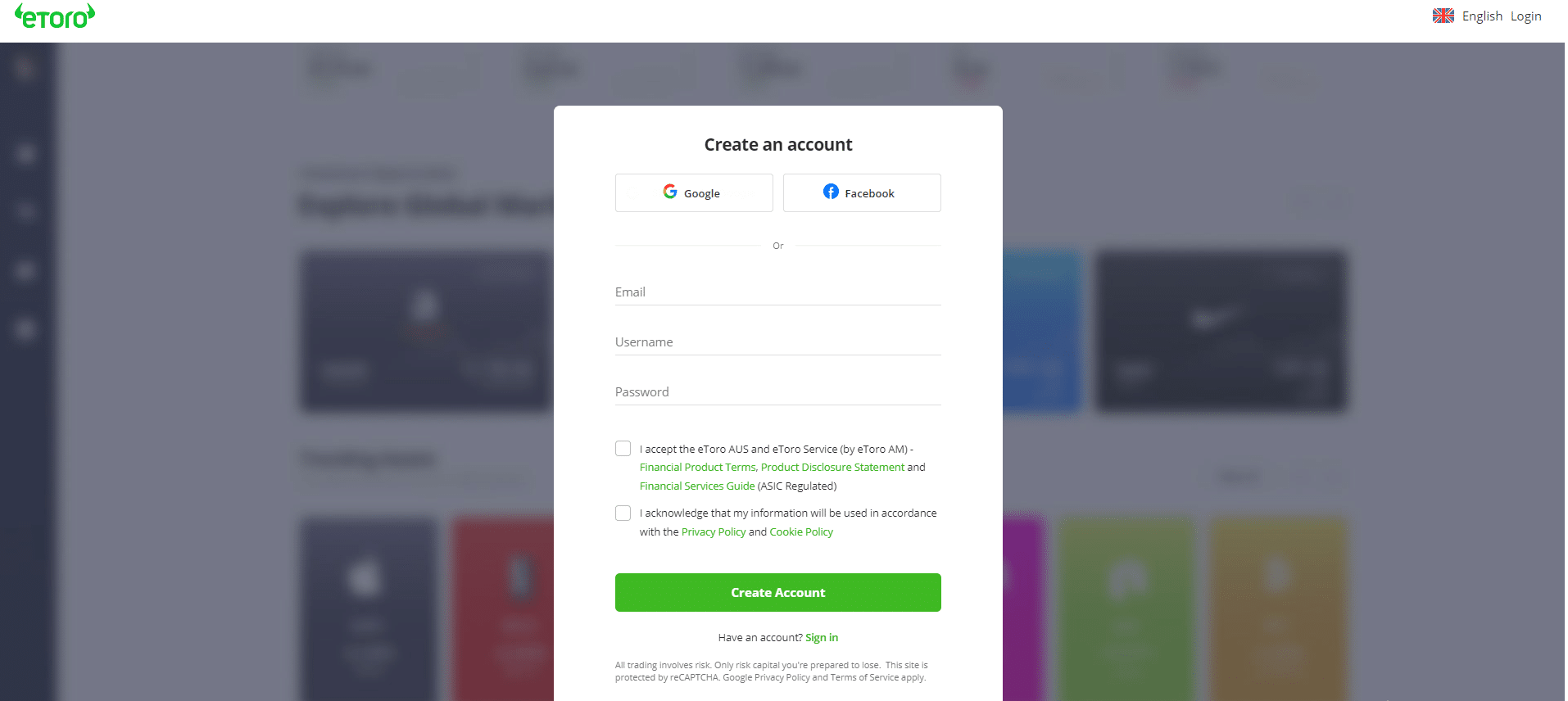
Step 1Register on eToro
Starting your journey on eToro requires creating a new trading account. Head to the official eToro website and click the green “Join eToro” button. Fill out the registration form on the next screen to complete the account registration process.
Step 2Verify Your Account
eToro requires every customer to undergo its Know Your Customer (KYC) process in line with industry compliance. Enter the required information to complete your profile.
Afterward, you must submit proof of identity and address documents to verify your identity and access the broker’s trading features.
Step 3Deposit Funds
Once the verification is successful, add funds to your eToro account using the “Deposit Funds” button on the user dashboard. The broker accepts deposits via bank transfer, credit/debit cards, and e-wallets like PayPal for US customers.
Choose a preferred payment method, fill in your banking details, enter the amount to deposit, and follow the on-screen prompts to complete the transaction.
Step 4Find Stocks
After the deposit arrives in your wallet, search for the stocks you’d like to trade on eToro using the platform’s search icon. Choose any of the thousands of securities and click on it to access the platform’s stock market.
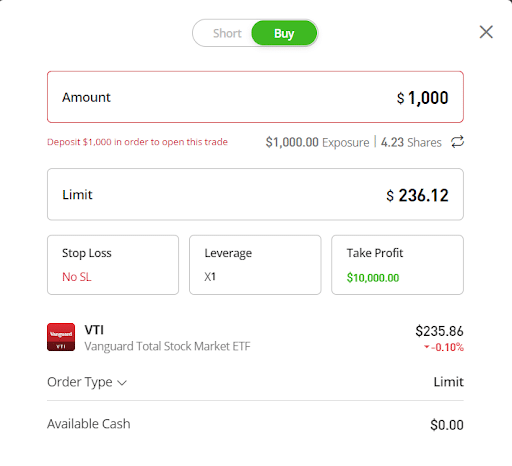
Step 5Start Trading with Limit Orders
Finally, click “Trade” and enter the required trading parameters in the dialogue boxes provided. These include the investment amount, order type, stop loss, and leverage. Check the transaction details and take a trading position.
Remember to combine your limit orders with a stop-loss to balance risks and rewards. You can also use eToro’s demo trading app to test your strategies.
What is a Limit Order in Stocks? – Conclusion
Now, we’ve come to the end of our detailed guide on “What is a limit order in stocks?” Trading with a limit order allows you to buy and sell a stock only at a preferred price. The trading tool is ideal for short and long-term traders looking to mitigate the risk of market volatility.
With over 30 million users worldwide, the lowest fees, and over 4500 tradeable assets, eToro is the best broker to consider for a diversified portfolio and stock trading using limit orders.
Your capital is at risk.
References
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/markets/stocks/news/navigating-market-volatility-11-strategies-for-successful-investments/articleshow/101040092.cms?from=mdr
- https://smartasset.com/investing/time-in-force
- https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/career-map/sell-side/capital-markets/slippage/
- https://www.rockwelltrading.com/articles/coffee-with-markus/day-orders-vs-good-till-canceled-orders-whats-the-difference/
- https://www.xetra.com/xetra-en/trading/order-types/execution-conditions
FAQs
How does a limit stock order work?
A limit stock order uses a predetermined price to buy or sell a security like stocks. The price is usually lower than the stock’s current price for buy limit orders and higher for sell orders.
Is a limit order a good idea?
Trading with a limit order can be a good idea for investors with a diversified portfolio of stock shares. The trading tool helps avoid slippage, trade at the best possible prices, and minimize losses.
What is an example of a buy limit order?
A buy limit order allows you to put a cap on the price you want to purchase a financial instrument. An example of a buy limit order is asking a broker to purchase an Apple Stock at $182.50 instead of $186.64.
What is the disadvantage of using a limit order?
The major disadvantage of limit orders is the failure to execute trades if a security’s price doesn’t reach the predetermined value. This can result in traders missing trading activities.
Why are limit orders risky?
Limit orders are risky because they don’t guarantee trade execution. When the market doesn’t move in your favor, a broker will not fill an order that doesn’t meet your price limits.
Adewunmi Adedayo
View all posts by Adewunmi AdedayoAdewunmi Adedayo is a seasoned finance and cryptocurrency writer with a passion for demystifying financial and crypto concepts to her readers. She has written several content for top websites such as IBtimes UK and The Nigerian Tribune. Adewunmi's style entails transforming technical topics into simple, captivating, and concise content for her audience.
stockapps.com has no intention that any of the information it provides is used for illegal purposes. It is your own personal responsibility to make sure that all age and other relevant requirements are adhered to before registering with a trading, investing or betting operator. Contracts for Difference (“CFDs”) are leveraged products and carry a significant risk of loss to your capital. Please ensure you fully understand the risks and seek independent advice.By continuing to use this website you agree to our terms and conditions and privacy policy.
Trading is risky and you might lose part, or all your capital invested. Information provided is for informational and educational purposes only and does not represent any type of financial advice and/or investment recommendation.
Crypto promotions on this site do not comply with the UK Financial Promotions Regime and is not intended for UK consumers.
© stockapps.com All Rights Reserved 2026
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.Scroll Up