What Is Scalping in Trading?

Day trading brought several earning opportunities, including the prominent scalping strategy. You can play it safe with long-term investments in blue-chip stocks or risk it with short-term volatile stocks. The latter leads you to scalping in trading, which occurs within daily trading hours.
Scalping stocks involves buying and selling them quickly to profit from small price swings. You can either buy and sell them for a higher price or a lower price, depending on what option you take. The scalping strategy applies to stocks, commodities, foreign exchange markets, etc.
-
-
Defining Scalping and its Objectives
Price movements are either in an uptrend or a downtrend. Sideways markets don’t present many opportunities to profit from price changes. Like many other investors, price changes, whether up or down, are the basis for profiting in the publicly traded market.
Short-term investors often opt for day trading, although some can hold their position for days. The scalping trading strategy is one way to profit from your price movement predictions. It is riskier than the average day trading but also more promising.
You’ll make several trades within one trading day. Regulations require more than $25,000 in your account to be eligible to take many trades in 24 hours. With that in perspective, let’s see the definition of scalping, its goals, and key characteristics.
Explanation of Scalping as a Trading Technique
Scalping in trading refers to opening and closing positions within minor price movements. Scalpers can place from 10 to 100 trades within a day. Also, you can scalp with call or put options as you would with other trading order types.
This technique requires substantial investments to generate meaningful profits. Moreover, short price swings will not result in jaw-dropping gains. Your gains on each trade might be less than 5%.
The Primary Goals of Scalping
You can wait for a stock to complete its uptrend before selling. Conversely, you can sell or close your position with little price movement and open new ones. The primary goal of scalping in trading is to profit from small price movements.
In a way, the technique looks safer than waiting for the stock or asset to complete its bullish run. Moreover, day trading carries risks because of the volatility. Still, the scalping trading strategy requires even more constant monitoring.
The holding time to scalp trade is often seconds or minutes. Notwithstanding, holding for hours is not strange, considering the stock market’s volatility. Some markets could move sideways for hours before hitting an uptrend.
Scalpers often do the following:
- Buy low and sell for a high price
- Buy high and sell for a higher price
- Short high and cover low
- Short low and cover lower
Key Characteristics of Scalping Strategies
The typical characteristics of scalping in trading include the following:
- It is fast-paced, even more than average day trading
- Execution must be properly timed
- It involves adjusting charts and indicators to small time frames
- Scalpers often use momentum indicators like the moving average convergence divergence (MACD), the stochastic oscillator, and the relative strength index (RSI).
- Price chart indicators are used to identify support and resistance levels.
- It requires substantial liquidity.
- Scalpers rely on technical analysis to predict price movements.
- It relies on automatic, instant order execution.
You’ll use the Level 2 window more to route your orders through the most liquid market makers.
The electronic communication network (ECN) is crucial for quick execution. That is because scalping in trading uses a point-and-execute style.
You might need to bypass brokers and trade directly with clients for sufficient speed. Direct Access Trading (DAT) is one way to achieve that and optimize the scalping strategy.
One trading day can bring several simultaneous trades. Hence, you must keep up with them to avoid losses. A slack in one trade can wipe off all your day profits.
Historical Context and Evolution of Scalping
This trading technique started before electronic trading. However, the execution speeds were slower than they are today. The concept of profiting from small price movements remains.
Origins of Scalping in Trading
It’s best to review history to lay some groundwork for what scalping in trading is. This technique began in the 19th century, when investors traded the open market for quick profits.
Investors had to go to the physical location (the open market) to scalp trade. However, trading was susceptible to speculation. That is because the open market had no regulation.
How Scalping Techniques Have Evolved
The invention of the telegraph in the mid-19th century allowed investors and brokers to communicate faster. This development increased trading volume and liquidity. Investors could execute faster trades and reduce the profit window. Still, the execution wasn’t brought down to seconds.
Electronic trading increased execution speeds. Still, investors didn’t have real-time monitoring like we do today.
Today, day trading apps can get you real-time updates for speedy executions. You can set up a robust trading station with several monitors to scalp trade efficiently. Moreover, you must be alert to avoid losses.
The Role of Technology in Scalping Practices
Technology helps achieve three essential things in trading today, as follows:
- Monitor the market in real-time
- Conduct technical analysis quickly
- Execute orders quickly
Level 2 windows provide comprehensive market orders. It is a step to optimizing your prices with Direct Market Access (DMA). However, this stage requires sufficient expertise and experience.
Timeframes and Chart Analysis in Scalping
Your trades will occur within minutes, prompting you to dial down your analysis to minutes. However, the short timeframes pose a challenge. The signals are less reliable than monitoring them for hours or even days.
Choosing Short Timeframes for Scalping
We recommend starting with higher timeframes and dialing back from there. For example, you can begin with 15-min, 10-min, or 5-min trading windows. These are more manageable, allowing for thorough analysis and reducing market noise.
1-minute timeframes produce more adrenaline. This speed puts you in emergency mode, something you must prepare to weather. Our recommended tips when choosing short timeframes include the following:
- Define your trading style and risk tolerance.
- Beginners should start with broader timeframes, like 15 minutes. You can go higher.
- Use multiple timeframes. For example, scalp trades on a 1-minute timeframe while monitoring and analyzing a 15-minute timeframe.
- Reduce your trading time as you gain expertise and confidence.
- Find timeframes with high liquidity and volatility. The idea is to get a market with enough price swings to generate profits within short intervals.
- Backtest your trading strategies.
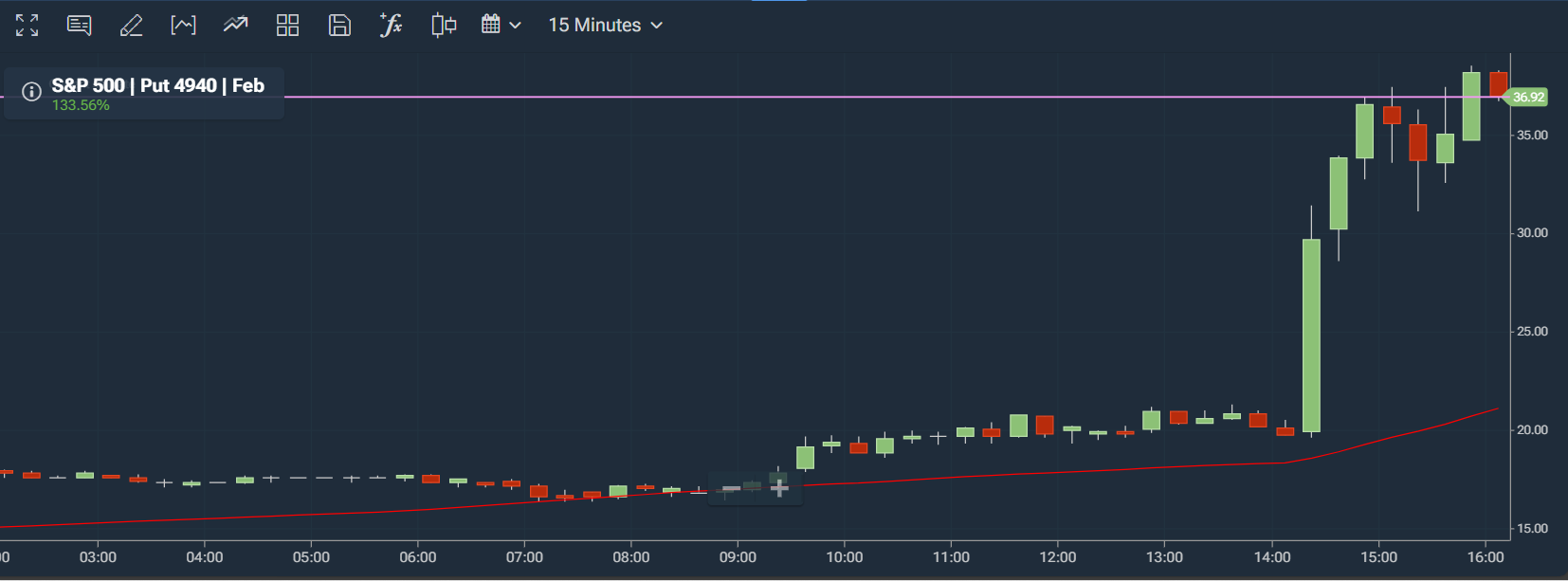
Reading Candlestick Patterns for Quick Decision-Making
The chart above is a typical candlestick pattern. We set it to a 15-minute window, but most platforms allow even more.
You can see that the price movement forms chart patterns as trading continues. You can use shapes to recognize patterns, but the approach becomes more ineffective with less time. For the most part, you will purchase stocks and wait for them to rise before selling.
Incorporating Technical Indicators for Precision
Charts show little information besides the price movements. Technical indicators expand the analysis, helping you identify momentum, trends, and entry and exit points. Typical indicators used in the scalping strategy include the following:
- The relative strength index
- The stochastic oscillator
- The Bollinger bands
- The moving averages
The Bollinger bands can help you identify overbought and oversold levels. They help spot trends and reversals and give ample signals to determine entry and exit points. However, you should spend at most 5 minutes scalping with Bollinger bands.
You can use the stochastic oscillator to forecast reversals. That can generate warning signs to exit your position before accumulating losses.
Moving averages can work in the short and long term. Short-term MAs highlight variations in price trends, while long-term MAs show an increasing or decreasing price trend.
Open the charts and switch to candlesticks. Then, click on the indicators to overlay them on the price charts.
Identifying Scalping Opportunities
You’ll find several price swings on a typical stock with high liquidity and volatility. However, knowing where to open and exit a trade requires more perspective.
Volatility and liquidity are prominent indicators of scalping opportunities. Technical analysis can also reveal trends and trading signals. With that in mind, let’s see how to identify and maximize these opportunities.
Recognizing Market Volatility and Liquidity
Scalping relies on quick price movements. You can catch volatility by glancing at a typical price chart. Reduce the timeframe to minutes and examine how frequently the price movement changes from red to green and vice versa.
The more volatility you have, the more scalping opportunities you’ll have. Volatility can come from economic news, geopolitical events, corporate earnings reports, market sentiment, etc.
High liquidity eases trade execution. You’ll enjoy minimal transaction costs and the opportunity to capture small price movements.
Analyzing Price Action for Entry and Exit Points
This approach relies on technical indicators to identify patterns and trends. You can use them to analyze support and resistance levels, shaping your trades around them.
Trading volumes can form an excellent combo with technical indicators. They will help you gauge market sentiment and how many willing buyers and sellers are available.
Utilizing Support and Resistance Levels in Scalping
These levels are crucial for entry and exit points. The support levels are where the stock price either goes sideways or reverses. Traders don’t expect stock prices to fall below the support levels, although it can happen.
Resistance levels show the maximum price a stock will climb to before reversing into the downtrend. The general approach is to buy when the price moves around the support level and to sell when the price moves around the resistance level.
You might not have perfect results based on support and resistance levels. Hence, you must combine this approach with other technical indicators. Ensure you trade at your acceptable risk level.
Risk Management in Scalping
Small profits can grow into substantial amounts through compounding. Similarly, one loss can erase your profits and reduce your equity. The key to avoiding that is managing risk while scalping.
Some traders have more risk tolerance than you. Hence, don’t invest money because another trader is investing the same amount. Stick with $2,000 if that is all you can spare without jeopardizing your daily survival.
Risk management begins with your orders. Fortunately, trading platforms incorporate a few features to help you minimize risks.
Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels
These functions are available when placing a new trade or opening a position. The stop-loss is the price (threshold) at which the broker will automatically sell your position when the stock price falls to that level.
For example, you can open a position at $100 and put a stop-loss order at $125. You’ll get $25 if the stock climbs above $125 but reverses and falls below the price.
Take-profit levels work the same way. However, you don’t wait until the stock price falls. The platform will automatically close your position once the price climbs to the specified level.
Stop-loss and take-profit levels are essential when scalping stocks. One eye away from the market can result in substantial losses. Hence, you should place those safeguards in place to minimize them.
Calculating Position Sizes for Minimal Risk
The position size refers to the number of units in an order. With little price movement comes the need to amplify your position for maximum profit. Hence, traders turn to leveraged trading when scalping.
You can calculate position sizes using the following methods:
- Percentage risk method
- Fixed-dollar risk method
- Volatility-based
The percentage-risk method entails how much you are willing to risk from your account. For example, a 2% risk from a $2,000 account will result in a $20 position size.
You can minimize risk by using the risk-reward ratio to determine your position size. The stop level must be outlined before finalizing how much to invest in a trade.
The Importance of Disciplined Risk-Reward Ratios
Higher risks bring higher rewards. However, risks can reach a point where you cannot bear them. Sitting down to determine how much you can lose is vital.
We recommend opting for ratios where the potential reward is greater than the risk. The optimal ratio should be 3% of your equity.
High-Frequency Trading Platforms
These platforms execute trades at high speeds and frequencies. They use complex algorithms to take advantage of small price increments. Then they buy and sell in large volumes to generate profit.
Hedge funds, institutional investors, and other large financial institutions often use high-frequency trading platforms. Notwithstanding, you can use them to your advantage. They require a learning curve, unlike regular trading platforms.
Features of Platforms Suitable for Scalping
Some platforms are more suitable for long-term investments. Here are some prominent features scalping platforms have:
- The execution speed should be fast, consistent, and reliable
- Transaction costs and commissions should be competitive
- Advanced charting capabilities
- Typical and advanced technical indicators and drawing tools
- Up-to-date news section for analysis
- Risk management functions like stop-loss and take-profits
Real-Time Data Feeds and Execution Speed
Platforms like MetaTrader 4 and 5 have real-time data feeds. You can see price changes every second as investors buy and sell the security or asset. These platforms allow customizations to show different feeds, depending on your approach to scalping.
Clicking on a stock, setting your position size and leverage, and adding risk management functions can be time-consuming. Fortunately, high-frequency trading platforms provide automation.
The Role of Automation in Scalping Strategies
Speed is essential to scalping in trading. Automation is the best way to reduce the time spent from setting up an order to executing it.
High-frequency trading platforms automate processes to achieve the following:
- Faster decision-making
- Faster order creation
- Faster order submission
- Faster order execution
Level 2 Quotes and Market Depth Analysis
Price charts from trading platforms do not show the thoughts behind the price movements. Level 2 quotes bring more detailed views of the market. It is essential to analyze the market in depth and see how the shares relate to the prices.
Level 2 quotes are often subscription-based. Hence, you might need to pay a premium to the trading platform or market to see its Level 2 quotes. Nasdaq is a prominent market that offers Level 2 quotes on subscriptions.
Understanding Level 2 Data for Informed Decisions
This data contains real-time bid and ask prices and trading volume. It has three components, as shown in the table below
Market Maker ID Price level Size The ID is a four-letter code corresponding to a specific market maker This section contains the price of the quote from each market maker This shows the number of shares the market maker intends to trade at that price level. The depth of the market and the number of shares available at each price point can help determine support and resistance levels. Review the number of shares at your preferred price level and those offered at higher price levels.
Level 2 data is not available for all stocks. Hence, confirm with your trading platform.
Analyzing Order Book Dynamics in Scalping
You can use the following approaches to analyze order books:
- Visualize the order book to see the market depth and the number of shares at each point.
- Monitor the spread (the difference between the bid and ask prices). You can gauge liquidity and volatility with this approach.
- Analyze the time and sales data to identify trends.
Incorporating Market Depth in Strategy Development
The market depth refers to its ability to absorb large orders without significant impacts on the price. Use it to determine support and resistance levels. You can also use it to assess the strength of prevailing trends and anticipate price movements.
Algorithmic Scalping and Quantitative Approaches
Trading platforms must use algorithms to achieve automation. This approach brings a hands-free operation and saves time you’d otherwise spend clicking your mouse. However, the approach has challenges worth exploring.
Overview of Algorithmic Scalping Techniques
These involve the use of computer programs to automate the following processes:
- Market data analysis
- Trading opportunity identification
- High-speed order execution
The systems use quantitative modeling and risk monitoring. Algorithmic scalping techniques work best when strongly trending action dominates the intra-day trade. It fails during periods of conflict or confusion.
Developing Quantitative Models for Scalping
Development begins by creating rules and algorithms for market data analysis. The process requires expertise. It includes the following steps:
- Understand market influencers like news, economic indicators, market sentiment, etc.
- Develop a trading strategy that defines your entry and exit points and your risk management strategies
- Collect historical price data
- Analyze the data
- Use mathematical and statistical formulas to predict future price movement
- Backtest the model to see its accuracy
- Refine the quantitative models and deploy them
Challenges and Considerations in Algorithmic Scalping
The challenges and considerations in algorithmic scalping include the following:
- Data quality
- The complexity of the quantitative model to capture market dynamics
- Latency in data access and transmission
- Changing market conditions
Psychological Aspects of Scalping
Trading will still be a rollercoaster, even with the best scalping strategies. You can make significant gains today and losses tomorrow. Notwithstanding, don’t lose your composure and confidence.
The key to acing scalping is dealing with stress, maintaining discipline, and avoiding psychological pitfalls. You must get your mind ready just as much as you do for your trading equipment.
Dealing with Stress and Quick Decision-Making
Here are some tips to minimize stress amidst quick decision-making:
- Have a trading plan for entry and exit points, stop-loss levels, and other risk management functions
- Minimize your losses with adequate risk management techniques
- Take regular breaks to ease the tension
- Automate your trading systems to take the decisions off you
- Use stock alert services to focus your news and updates
Maintaining Emotional Discipline in Scalping
Several emotions can swing by within one day when scalping in trading. The best way to keep them in check is to have defined systems or approaches for everything. Refine and backtest your strategies instead of whining about them.
Learn more about scalping in trading, especially algorithmic techniques and quantitative models. Education never ends, especially when automating your trading process. Be flexible to accommodate market changes quickly
Psychological Pitfalls to Avoid in Scalping
The following are psychological pitfalls to avoid in scalping:
- Pursuing losses by increasing your position size for the next trade
- Taking too much leverage to amplify your position size
- Overconfidence
- Trading more markets than you can handle
- Entering trades impatiently and randomly because you want to be fast
- Fear and greed
- Trading without discipline
- Amplifying your position to negate previous losses
Broker Selection for Scalping
The trading software is as important as the hardware. Scalping’s fast-paced trading environment requires robust trading platforms to handle quick executions. Automation should also be available to quicken the process and ease the tension.
Features to Look for in Scalping-Friendly Brokers
Here are prominent features you must consider in scalping-friendly brokers:
- Low latency for fast trade executions
- Tight spreads to maximize profit
- Low commissions because of multiple daily trades
- Reliability
- Adequate holding periods and maximum trade durations that favor scalpers
- Advanced charting tools
Most importantly, the broker should accommodate algorithmic techniques and quantitative models. These will hasten your trading process.
Evaluating Commissions and Execution Speed
Scalping can involve up to 100 trades daily. A high commission is discouraging, especially as the number of trades increases. These charges might eat into your profits, reducing them and negating your daily profits.
Low-commission platforms are best for scalping. They take little, allowing you to continue trading as much as possible.
Execution speed must be stellar. That means the user interface and navigation should be buttery smooth. One mouse click should produce an instant order placement, sell or buy.
The Importance of Reliable Order Execution
Scalping relies heavily on time. A split second can mean a missed entry point or a late exit. Hence, reliable order execution is non-negotiable for the broker.
Besides the trading platform, ensure your device is speedy enough. Invest in your trading setup to get the best experience.
Scalping in Various Market Conditions
Flexibility is crucial when scalping in trading. That is because market trends can change and momentum can shift. Hence, you should be ready to adapt your algorithms and quantitative models to the new conditions.
Adapting Scalping Strategies to Different Market Trends
Markets can either be trending, range-bound, or volatile. Identify the trend direction and ride the momentum. Range-bound markets require a different approach.
Identify support and resistance levels during range-bound markets and trade within the price fluctuations. When volatility hits, adjust your strategy to mitigate the risks.
Scalping During News Releases and Economic Events
News releases and economic events might destabilize the market. Reduce your scalping approaches during periods of conflict or confusion. However, if the news releases are positive, warm up for even more trading sessions.
Strategies for Navigating Low-Liquidity Conditions
Low liquidity is challenging even for the best scalping strategy. Nonetheless, you can do the following to navigate it:
- Avoid volatile markets during this period
- Pause scalping and focus on longer-term trades
Best Stocks for Scalping Trading
The following are the best stocks for scalping:
Tesla (TSLA)
The stock price sank after the company posted disappointing fourth-quarter results. However, past performance between 2022 and 2023 shows massive upside potential.
Amazon (AMZN)
Analysts have positive reviews about Amazon and its stance for 2024. Most recommended it as a strong buy for the season.
Uber Technologies (UBER)
This company has quietly racked up its appeal in the stock market. It maintained an uptrend into 2024 and is poised to continue.
Mastercard (MA)
This stock has liquidity and price swings suitable for scalping. More so, it’s ridden an upward trend from November 2023 to January 2024.
Discover Financial Services (DFS)
The price movement has shown enough swings for scalping. However, it requires extra attention to accommodate its volatility.
Recap of Key Insights into Scalping in Trading
- Scalping involves making quick trades to profit from small price movements.
- You can make as many as 100 trades a day.
- Understanding candlestick patterns is necessary for quick decisions.
- Technical indicators are necessary to identify trends and momentum.
- Volatility and liquidity present scalping opportunities.
- Stop-loss and take-profit levels are crucial to minimizing losses.
Conclusion
Scalping in trading involves making short-term trades to capitalize on small price movements. You need a sufficient position size to make reasonable profits. Nonetheless, the key to scalping is the compounding effect of multiple short-term trades.
References
- https://www.zippia.com/stock-trader-jobs/demographics/
- https://www.protradingschool.com/how-do-you-handle-trading-stress/
- https://markets.businessinsider.com/news/stocks/day-trader-made-million-lost-it-all-cautionary-tale-investing-2020-7-1029383192
- https://moneyinc.com/richest-day-trader/
- https://nasdaqtrader.com/Trader.aspx?id=NQDS
FAQs
How does scalping trading work?
This strategy works by placing quick trades (a few seconds or minutes) to capitalize on small price swings.
Is scalping good for beginners?
The technique can be intense for beginners. We recommend starting with 15-minute intervals before reducing the timeframe.
Is scalp trading illegal?
This strategy is legal and popular among day traders. The profits from quick trades add up to significant amounts.
Can scalping make you a millionaire?
Scalping is effective in profiting from stock market trading. However, you need sufficient equity and multiple trades for reasonable profits.
Why don’t brokers like scalping?
The profits from individual trades are often small because of the small price movements. However, the trade volume or orders may strain broker systems.
Jeremiah Awogboro
View all posts by Jeremiah AwogboroJeremiah Awogboro is an experienced content writer with over 8 years of experience. He has a qualified MBChB degree and a keen interest in the stock market and the finance industry. His background in the industry has provided him with valuable experience in this field. Awogboro is dedicated to assisting and reaching out to as many people as possible through his writing. In his spare time, he enjoys music, football, traveling, and reading.
stockapps.com has no intention that any of the information it provides is used for illegal purposes. It is your own personal responsibility to make sure that all age and other relevant requirements are adhered to before registering with a trading, investing or betting operator. Contracts for Difference (“CFDs”) are leveraged products and carry a significant risk of loss to your capital. Please ensure you fully understand the risks and seek independent advice.By continuing to use this website you agree to our terms and conditions and privacy policy.
Crypto promotions on this site do not comply with the UK Financial Promotions Regime and is not intended for UK consumers.
© stockapps.com All Rights Reserved 2024
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.OkScroll Up