What Are Small Cap Stocks And Should You Invest Into Them?

Publicly traded companies sell their shares to the public, including restricted shares that require permission. You can use these sales to assess a company’s worth, whether it has a small-cap stock value or higher. The more money a company can generate from its share sales, the higher its market capitalization among rivals.
While others wonder what small-cap stocks are, we’ll review this concept and how it can aid your trading decisions. This guide will begin with the market cap meaning and how small-cap stocks come about. With that in mind, let’s understand the market cap’s definition and significance in trading.
-
-
-
-
Definition and Characteristics of Small Cap Stocks
Valuators consider a company’s debt and assets to compute its value or worth if someone were to buy it. That works ideally for private companies that do not sell their shares publicly. However, we can consider a company’s outstanding shares to guess its worth.
Apple is the largest company in the world currently, with a $2.99 trillion market cap. That might change in the next few months. While the change is not our concern today, you can see why people opt for Apply shares instead of Prometheus Biosciences.
A company’s outstanding shares cover those sold publicly and those with restricted sales. With that in mind, let’s answer the pending question, What are small-cap stocks?
Defining Small Cap Stocks by Market Capitalization?
Market capitalization refers to the total market value (in dollars) derived from selling a company’s shares. Let’s assume Company A has 1 million shares at $200. The market capitalization equals $200 million (1 million * $200).
We can shorten capitalization and call it market cap. You’ll see the two words interchangeably in this guide.
The above market cap formula is simple. However, those who use day-trading apps know that a company’s share fluctuates in price.
With that in mind, small-cap stocks refer to companies with market capitalizations ranging from $250 million to $2 billion. The opposite of small-cap stocks is large-cap stocks. Apple is a prominent example in the latter category.
Seasoned investors understand the opportunities in investing in small-cap stocks. We’ve given a preliminary definition of what a small-cap stock is. Nonetheless, sorting through the many options and adding the best small-cap stocks to your trades is crucial.
We’ll explain how to research stocks in this category. Then, you can add them to your portfolio.
Key Characteristics of Small-Cap Companies
Having less than $2 billion in market capitalization doesn’t mean a company is doing poorly. The opposite might be the case. With that in mind, here are a few prominent characteristics of small-cap companies:
- Less publicity: The media prefers to focus on Apple, Google, Microsoft, Blackrock, etc., because of their size and far-reaching influence. That leaves little attention to small-cap companies. Hence, don’t expect to see them on the news 24/7, except when they do something groundbreaking.
- High growth: Companies in this segment have the potential for quick growth. They are often emerging industries with disruptive ideas. Investors consider them the large-cap companies of the future.
- Lower liquidity: You might not quickly find buyers and sellers compared to large-cap companies. That results in lower liquidity.
- Less financial cushions: Crisis, regulations, and poor management can easily wipe out small-cap companies. That is because of the lower financial flow needed to cushion the company during the financial crises.
- Higher volatility: A lower financial base means more sensitivity to market changes. That makes small-cap companies more volatile.
Your capital is at risk
Differentiating Small Caps from Mid and Large Caps
The table below compares small caps with mid and large caps:
Parameter Small caps Mid caps Large caps Capitalization $250 million to $2 billion $2 billion to $10 billion Above $10 billion Investors Less institutional investors Moderate institutional investors High institutional investors Phase Growth phase Expansion phase Matured phase Trading volume Low Moderate High The Appeal of Small-Cap Investments
Some traders would rather avoid volatility, opting for something more stable. They gravitate towards large-cap companies. While this article is not a large-cap vs. small-cap debate, we recommend basing your decision on your trading goals.
The higher the risk, the higher the reward. This mantra applies to stock analysis, as more volatile stocks yield more gains. That is where the appeal for small-cap investments hinges.
Small-cap companies can grow to become large-cap enterprises. For example, Microsoft grew from a $777 million capitalization in 1986 to $2.89 trillion today. Hence, small-cap investments appeal to short- and long-term traders/investors.
Growth Potential and Market Outperformance
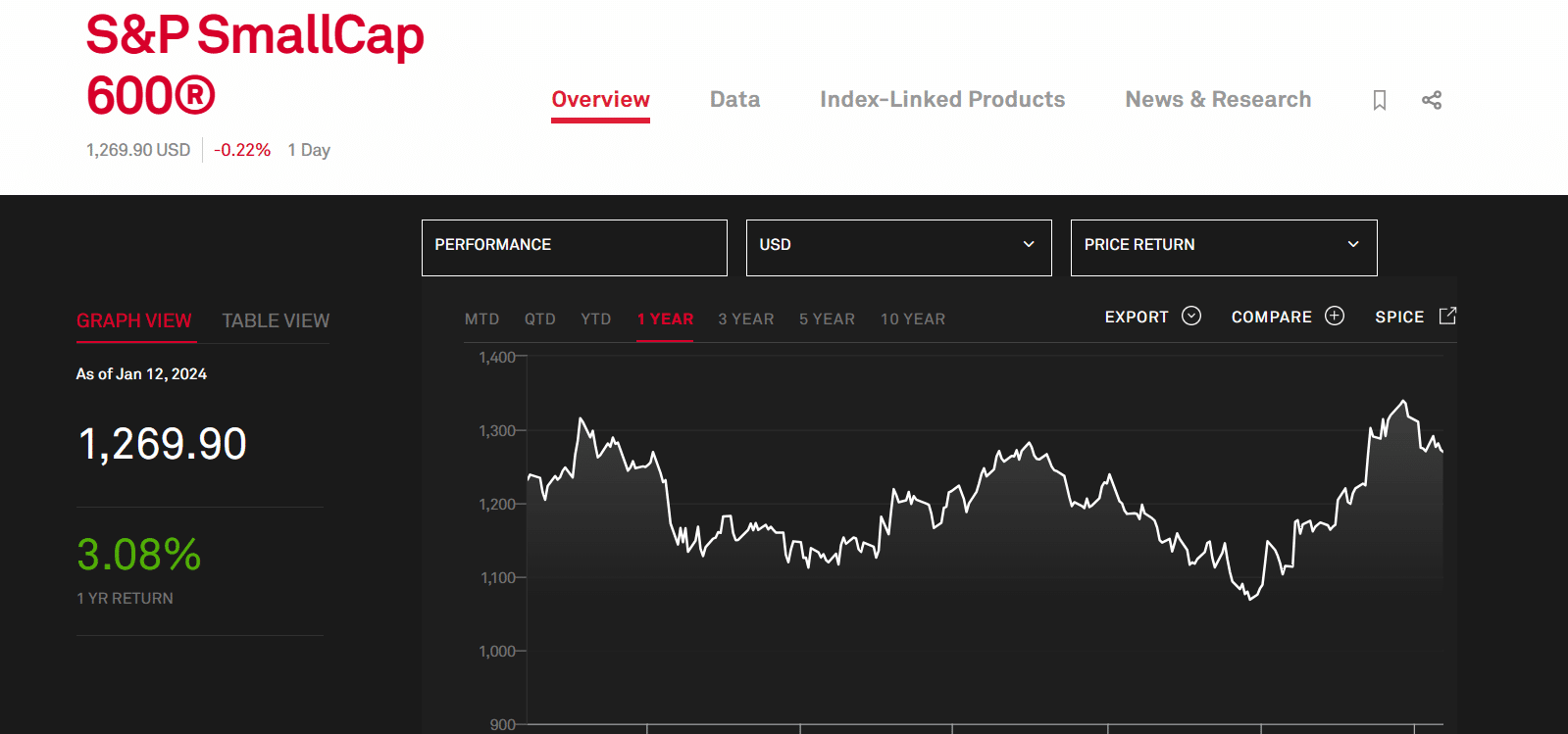
The S&P SmallCap 600 is a prominent index to follow the performance of small-cap companies. You can also refer to the Russell 2000 index for data on the smallest companies in the US. We recommend them if you want small companies to invest in.
Reports show that small-cap companies have outperformed those in the mid and large-cap categories for the past 20 years. They returned 8.3% annually, compared to 8% and 6.3% from the mid and large-cap categories, respectively.
The report above reveals the growth potential of small businesses. They are better positioned for growth, and most activities will focus on growth. Also, you can expect higher share prices as they become well-known nationally and globally.
This growth presents investment opportunities. Those willing to bear the volatility risk can get significant returns on their investments. These can come from dividend payments or higher share prices.
Agility and Adaptability in Small-Cap Companies
Agile teams adapt quickly and can pivot companies into more profitable areas. They are more prominent in small-cap companies, where operations are more adaptable. Also, fewer bureaucracies allow small businesses to respond more quickly to changes than large enterprises.
Adaptability and agility can yield faster growth and prominence. These increase the profit margins, helping the company attain higher values. Therefore, those who invest early can reap from the expedited growth.
You can gauge a company’s adaptability through thorough stock market research and analysis. Increasing stock prices often accompany these businesses.
Opportunities for Early Investors and Market Niches
Small companies often come in through market niches. For example, Dbrand doesn’t make smartphones, which is an industry that Samsung, Apple, Xiaomi, Motorola, etc. dominate. They focus on a niche market, the cases.
These niche companies grow to become titans in their industries. Hence, early investors smile at the bank as their investments double, triple, or even increase.
The opportunity to break new ground and become a dominant power makes small-cap stocks appealing. Investors would weather the risk of failure if the yield could be rewarding.
Your capital is at risk
Potential for High Returns
Past performance does not guarantee similar future results. However, most analysts base their projections partly on past performance.
With small-cap stocks, the potential for high returns remains. These high returns come with associated risks that most conservative traders would avoid. The uncertainty can cause an emotional roller-coaster for the unprepared.
We’ve explored what small-cap stocks are, but let’s see how they’ve performed. That’ll further explain its appeal for short- and long-term investments.
Historical Performance of Small Cap Stocks
Small-cap stocks graced a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12% from 1972 to 2021. That was 0.9% higher than what the large-cap stocks did. You can refer to Portfolio Visualizer for the data, as other historical datasets have shorter periods.
Aswath Damodaran pointed out that small-cap stocks have outperformed large-cap stocks during periods of high inflation. The former correlated better with inflation than the latter. Also, smaller companies respond quicker to economic changes.
Correlation Between Risk and Return in Small Caps
Smaller companies have more room for growth. Hence, their returns can be higher than those of larger companies.
The higher returns come with more risk. Risk and return are positively correlated. That means an increase in risk yields an increase in return.
We can’t be confident in small-cap companies’ ability to weather economic downturns like large companies would. They have less cash flow, which impacts their rooting during economic downturns. Also, their reliance on borrowing could strain their resources during high-interest rates.
Most traders rely on alternative data sources to capture what the trading charts won’t show you. These can reveal associated risks and market sentiment toward a stock.
Identifying Growth Catalysts in Small-Cap Companies
The best small-cap stocks don’t happen overnight. Growth catalysts are central to the high growth rates small-cap companies often experience.
A few examples of growth catalysts include the following:
- New product launches: Disruptive product launches heavily influence growth. These show investors the potential for market dominance in years to come. Also, they increase the company’s credibility and worth in the public eye.
- Management appointments: The presence of a well-known executive at a small company lends it credibility and increases its worth. For example, Susan Wojcicki was a former YouTube CEO who joined 23andMe.
- Earnings: Increased earnings often lead to increased stock prices. It sends positive signals to the market, proving the company’s performance and readiness for growth. Hence, the demand for its stocks increases.
- Acquisitions: Large companies can acquire small, promising businesses. These acquisitions often result in higher stock prices as investors brace for increased growth.
You can also look for mergers and industry tailwinds. The latter covers businesses that are in high-growth industries.
Partnerships and new markets can catapult companies to higher returns. Again, you should use alternative data sources and news channels to monitor these aspects.
Volatility and Market Risks
Those who know what small-cap stocks are focus on volatility. They might not be as volatile as what you’ll see in the crypto industry. However, their volatility is enough to carry significant risk for investors.
We’ll discuss timing and exit strategies to deal with small-cap stock volatility soon. In the meantime, let’s explore what makes a small-cap value volatile and the factors that influence it.
Understanding the Inherent Volatility of Small Cap Stocks
Business cycles include rough patches. Also, profitability is an issue for small-cap stocks, which are often in their early stages. That leaves uncertainty for investors and the public.
Uptrends in small-cap stocks are often due to growth catalysts like disruptive product launches. The public dives in, causing stock prices to increase. However, the excitement dies when other companies release competing and more stable products.
The public’s perception relies heavily on what the company does. Earning reports, new appointments, partnerships, acquisitions, etc., can increase the stock’s perception.
External Market Factors Impacting Small Caps
Large caps can weather external economic storms better. They have better financial standing and market trust. That brings us to external market factors that impact small caps. These include the following:
- Economic changes: Interest rates, consumer confidence, inflation, etc., are prominent economic factors that influence small-cap shares.
- Regulations: The government can revise old laws or make new ones. For example, the US ban on Huawei affected several companies that relied on it as a supplier and buyer. Larger companies weathered the ban better, but we can’t say the same about small companies that relied on Huawei parts.
- Industry trends: New technology or consumer preferences can impact small caps negatively. They can drive public sentiment away from small companies as they lag.
Small-cap companies may split their stocks if the price increases way beyond that of their industry peers. That will result in more market shares, although the capitalization will stay the same. Nonetheless, increased investor sentiment can cause and increase in the share price.
Navigating Through Economic Downturns and Market Fluctuations
Companies have various ways to deal with economic downturns and market fluctuations. Many tech giants, including Meta, Twitter (now X), Amazon, and Google, cut jobs in response to the new economic realities in 2022/2023. Still, these companies have cash flow to stay in business.
Small companies may not be privy to such cash flows. Hence, they can scale back their operations, resulting in a loss of public confidence. The latter drives their stocks down as demand decreases.
Economic downturns and market fluctuations cause uncertainty. Most traders would hold their positions or avoid buying stocks during these periods. Again, the decrease in demand leads to lower share prices for small-cap businesses.
Your capital is at risk
Liquidity and Accessibility Challenges
Money makes trading go around. The less money people invest, the lower the trading volume. That is why large-cap companies often have high trading volumes.
Liquidity and accessibility are integral to market capitalization. The former refers to how much traders and investors commit to stocks, while the latter refers to how easily traders can find the stocks.
Impact of Lower Liquidity on Small-Cap Investments
We can summarize the impact of lower liquidity on small-cap investments as the following:
- Fewer buyers and sellers in the market make it challenging to trade
- Broader bid-ask spreads
- Increased trading costs result in lower returns
- Increased volatility
The less money the stock market has, the more volatile it becomes. Hence, lower liquidity can cause even the tiniest trades to influence prices massively.
Challenges in Executing Trades and Managing Positions
Small-cap companies are less prominent. As mentioned in the previous section, the number of buyers and sellers is relatively small. Finding a buyer or seller becomes challenging.
Most online brokers may not include the stock in their trading instruments. That makes it challenging to execute trades or hold your position.
Brokerage Considerations for Small-Cap Investors
Trading small-cap stocks goes beyond clicking the buy and sell buttons. The online brokerage industry plays a pivotal role. Hence, you must consider a few things before settling for a platform.
We’ve identified research tools and trading fees as prominent brokerage considerations for small-cap stocks. The more research tools you have, the better informed your decisions will be. Similarly, lower trading fees leave higher returns for you.
Fundamental Analysis for Small-Cap Investments
We won’t delve much into the technical analysis of small-cap investments. You can read our articles in the education section to learn about technical tools and how to use them. In the meantime, we’ll review the primary considerations for analyzing small-cap stocks before investing.
Evaluating Financial Health and Stability
Good financial health brings positive market sentiment. Once that happens, traders are happy to buy and sell the company’s stocks. Conversely, finding buyers becomes challenging when the company becomes financially desperate.
You can refer to the SEC filings to analyze a company’s financial health. We don’t expect companies to publish their finances when operating at a loss.
Invest in companies with good financial health and some level of stability. The market might be volatile, but finding its balance after wild price swings takes little time.
Examine the company’s debts and income statements. That reveals when they are in chronic debt or profiting. Don’t expect new companies to be profitable during their early years.
Assessing Management Competence and Corporate Governance
You can gauge a management’s competence from its decisions and policies. This section requires finding news on significant decisions like product launches, partnerships, licenses, etc.
We recommend going further to look up information about the management staff. CEOs are often famous. Ask the following questions when reviewing the management team:
- Have the company’s prominent leaders managed other successful companies before?
- Is the management involved in any scandal?
- Is there any management staff in dispute with the law?
You don’t need to write off anybody at face value. For example, a new CEO who has never managed a mega company can perform excellently.
Analyzing Market Potential and Competitive Landscape
Most small-cap companies enter already-existing markets. That brings them into competition with other emerging and established companies. Competition determines the probability of success.
Refer to the company’s unique selling point when evaluating its market potential. You can review sales figures to gauge its acceptance by the public.
Compare the company’s performance with competitors. You can overlay them and see which one has more credibility and acceptance in the market.
This stage doesn’t require overly technical tools. Notwithstanding, they can be helpful for quicker analysis.
Diversification and Risk Management
Some companies grow faster than others, and some are more volatile than others. This market reality highlights the need for diversification and risk management. Putting your money into one stock can be a recipe for losses.
Building a Diversified Small Cap Portfolio
Diversifying your small-cap portfolio means investing in different small-cap stocks. These companies can come from different sectors or industries. The important thing is having a healthy mix.
Go to the S&P SmallCap 600 or the Russell 2000 index to find small-cap stocks. Review their performance to get the best small-cap stocks for your portfolio. You can use AI stock-picking tools for quicker results.
The next step is to find brokers that offer your preferred stocks. Buy them and add them to your portfolio. Then, trade as you want or hold your position for long-term trades.
You can add value stocks and more speculative growth options to the portfolio. Mix volatile and less volatile stocks. Spend more money on the less volatile options to offset potential losses on the more volatile ones.
Setting Realistic Expectations and Investment Goals
Diversification begins with setting your investment goals. Tesla’s stock may have jumped over 100% in 2023, but that does not mean all companies will have the same experience. Realistically, it would be unwise to peg your expectations at 100% growth.
Chart analysis will help you determine what to expect. Moreover, trading is not a one-off click experience. You must monitor the market to exit it promptly.
Begin by determining your risk tolerance. Then, align your trading timelines and resource allocations accordingly. You can review AI predictions and expert projections when investing.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks in Small Cap Investments
The following are strategies to mitigate risks in small-cap investments:
- Trade stocks across different sectors and industries
- Set stop-loss orders to limit your losses during market crashes
- Look for momentums through increased trading volumes (most trading platforms have tools to display trading volumes)
- Hedge your trades with counter positions (for example, you can open short and long positions)
Your capital is at risk
Timing and Exit Strategies
All traders would agree that time is crucial in trading. Exiting a position now could spare you heavy losses in the next few minutes. Of course, most trading platforms, like eToro, have tools to protect you, but you must do your due diligence.
Recognizing Entry Points for Small Cap Investments
We’d probably avoid entering a trading position when a stock is completing its bullish run and turning around to become bearish. Trading charts give an overview of the price movements.
We recommend using technical indicators to identify entry points. These include the following:
- Moving averages
- Bollinger bands
- Relative strength index
- The MACD indicator
- The supertrend indicator
You can read about them on our website and practice with eToro. These tools will help you identify when the sentiment is strong or weak.
Monitoring and Adjusting Positions Based on Market Conditions
The next step is keeping an eye on the market. Tools like stop-loss orders and take-profits can help you minimize losses. However, they don’t stop you from watching the market.
Day traders monitor the market closely. You might not need much frequency if you are entering a position for the long term (weeks or months). Notwithstanding, monitoring helps you do the following:
- Identify opportunities to reinforce your position
- Identify points to adjust your position
Assessing When to Take Profits or Cut Losses
This decision is entirely up to you and your investment goals. Sometimes, pursuing more profits can end in a loss.
Bullish runs increase your profits, but they won’t continue forever. Similarly, waiting for swings during bearish markets might lead to more losses. You must assess when to cut your losses or take your profits.
Here are our recommendations:
- Sell your stock when you lose 7% or 8% below the purchase price
- Use a 3:1 to sell during bull runs (Allow 1% losses for every 3% gain)
Losing 10% doesn’t mean you need 10% to regain your losses. Contrarily, you’ll need 11.1%. Let’s do some math with a $100 stock that fell to $90.
10% of $90 = $9 (this isn’t enough to get back $100).
You need a $10 gain to get back $100. $10 of $90 is as follows:
= (10/90) * 100
= 11.1%
With that in mind, cutting losses below 8% is better. Don’t wait too long to sell.
Investment Horizon and Risk Tolerance
Consider the time you want. Day traders and long-term investors have different strategies and risk tolerances. The latter can bear multiple losses while expecting the market to grow in the long run.
Aligning Small Cap Investments with Personal Goals
Small-cap companies can eventually turn into large businesses. That means you can invest and hold your investment for years without selling.
Consider your personal goals. Pick day trades if you prefer making a profit from short price bursts. Otherwise, pick long-term trades for yearly gains as the company grows.
Assessing Risk Tolerance for Volatile Markets
Volatile markets are riskier. Consider how much you can lose before investing. Also, you can try other trading options, like betting against the market.
Balancing Small Caps within a Diversified Portfolio
Your portfolio can have small caps and blue-chip stocks. The former is riskier, hence the need to invest smaller amounts. Blue-chip stocks are less volatile and more predictable.
Invest larger amounts in blue-chip stocks. Use the hedging technique to offset losses in your portfolio. Most importantly, use a portfolio tracker to keep up with new developments.
Due Diligence and Research Checklist
This guide is part of the journey. You still need more research on small-cap companies to determine if they are worth your investments. We’ve developed a checklist to help you scrutinize small-cap stocks before investing.
Importance of Thorough Research Before Investing
Thorough research offers the following benefits:
- It helps identify scams (some companies make empty promises without market-ready products).
- You’ll learn about the company’s performance and industry trends
- It helps identify undervalued companies with robust growth potential
- It helps identify the risks of investing in a company
Key Metrics to Scrutinize in Small Cap Analysis
The following are the key metrics to scrutinize:
- Revenue growth from inception
- The current profit margins
- The company’s debt
- The company’s valuation
- The competition in the industry
- The company’s positioning towards industry trends
Learning from Successes and Failures in Small-Cap Investing
We can’t promise that all your trades will be successful. Preparing yourself for losses is best. Hence, we recommend investing your spare cash or an amount you are comfortable losing.
Your capital is at risk
Summary of Small Cap Opportunities and Risks
The following summarizes our points on small-cap opportunities and risks:
- Small-cap companies have high growth potential
- High growth potential brings opportunities for short-term profits.
- Long-term investments can be profitable as these companies grow into large businesses (expanding into the mid- and large-cap segments)
- The small-cap market is more volatile
What are Small Cap Stocks? – eToro Complete Guide
Small-cap stocks are risky. Hence, we don’t recommend jumping into trades until you’ve reviewed the market thoroughly and tested a few trading strategies. eToro is the ideal trading platform to start trading without spending real money.
For illustration purpose only
This broker offers a $100,000 virtual account to get you up and running. Follow the steps below to register and set up your eToro account:
Step 1: Open the eToro websiteUse our links to open the official eToro web page. You can do that on your PC or smartphone. Download the mobile app from the homepage according to your device.
Click the “Join Now” or “Join eToro” button on the homepage. That will open the registration page for you to fill out your details.
Step 2: Provide your registration detailseToro has a one-page registration to set you up quickly. Enter your username, email, and password. Then, agree to the privacy policy and the terms of service to complete the registration.
Click “Register” to close the registration page. Ensure you use a valid email for the verification code.
Step 3: Verify your email and log in.The registration should redirect automatically to the verification page. Enter the email verification code to complete your registration.
Step 4: Verify your identityYou can access the $100,000 virtual account without verifying your identity. However, we recommend completing this process to deposit money into your account.
Go to your profile and upload the required documents. Provide other details before uploading the documents.
Step 5: Load the trading dashboardUse the virtual account or switch to real-money trades. Load the dashboard and pick the stock you want. Review the charts and start trading.
Conclusion
Small-cap stocks come from companies with a $250 million to $2 billion market capitalization. They are often new to the scene and have high growth potential. Furthermore, you can invest for short- or long-term profits.
Set your investment goals and invest according to your risk tolerance. Use reputable trading platforms like eToro.
Your capital is at risk
References
- https://www.statista.com/statistics/263264/top-companies-in-the-world-by-market-capitalization/#
- https://www.spglobal.com/spdji/en/indices/equity/sp-600/#overview
- https://www.portfoliovisualizer.com/backtest-asset-class-allocation
- https://www.cnet.com/tech/mobile/huawei-says-blacklisting-will-significantly-harm-american-companies-jobs/
FAQs
What is considered a small-cap stock?
A small-cap stock belongs to a company with a market capitalization between $250 million and $2 billion.
How risky are small-cap stocks?
These companies have less cash flow to be stable during economic storms. Hence, they are more volatile than large companies. This presents a risk for short-term investments.
Is it a good idea to invest in small-cap?
You can profit from small-cap investments. However, you must scrutinize the company, diversify your portfolio, and time your entry and exit points.
What are the disadvantages of small-cap stocks?
The disadvantages include relatively higher volatility, less liquidity, more challenging access, etc.
Why do people invest in small-cap stocks?
Some people invest for the long term, hoping that small-cap stocks will become blue-chip options (large companies). Others use the high growth potential to profit from quick price swings.
Jeremiah Awogboro
View all posts by Jeremiah AwogboroJeremiah Awogboro is an experienced content writer with over 8 years of experience. He has a qualified MBChB degree and a keen interest in the stock market and the finance industry. His background in the industry has provided him with valuable experience in this field. Awogboro is dedicated to assisting and reaching out to as many people as possible through his writing. In his spare time, he enjoys music, football, traveling, and reading.
VISIT ETOROYour capital is at risk. Other fees apply. For more information, visit etoro.com/trading/fees.stockapps.com has no intention that any of the information it provides is used for illegal purposes. It is your own personal responsibility to make sure that all age and other relevant requirements are adhered to before registering with a trading, investing or betting operator. Contracts for Difference (“CFDs”) are leveraged products and carry a significant risk of loss to your capital. Please ensure you fully understand the risks and seek independent advice.By continuing to use this website you agree to our terms and conditions and privacy policy.
Trading is risky and you might lose part, or all your capital invested. Information provided is for informational and educational purposes only and does not represent any type of financial advice and/or investment recommendation.
Crypto promotions on this site do not comply with the UK Financial Promotions Regime and is not intended for UK consumers.
© stockapps.com All Rights Reserved 2025
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.OkScroll Up