What is Float in Stocks?
Stocks offer you the opportunity to own equity in a company. At the same time, they double as short and long-term investments, depending on your financial goals and preferences. However, stocks come in different types, and a floating stock is a category of a company’s shares you can buy and sell.
This type of stock is a company’s regular shares available to the public for trading in the open market. Still not clear on what is float in stocks? Our guide explores the stock type and why it matters to investors.
[toc]Key Takeaways
Stock Float Definition
Understanding how stock float works can help determine if it’s a suitable investment. We dive into the details of the stock variant in the following sections.
What is Stock Float?
A stock float is a company’s basic shares that it issues to the public for trading purposes. Floating shares are available on the open market, so retail and institutional investors can trade them on stock investment apps.
You may wonder how stock floats are different from other stock types. In simple terms, the floating stock is the total number of shares of a company’s stock available to traders in the open market. It represents a firm’s remaining stocks or shares after deducting its restricted stocks and closely held shares from its outstanding shares.
Restricted stocks are a firm’s shares that cannot be traded or transferred to shareholders until certain conditions are met. For instance, when a company sells its first public share through an initial public offering (IPO) and has a lock-up period, its stocks are temporarily restricted.
Conversely, closely held shares are stocks owned by a company’s major stakeholders. These include insiders, employees, and significant shareholders. The company can also limit the trading of closely held stocks with a lock-up period. Besides these two stock categories, whatever is left of a company’s outstanding shares makes up its public float stocks.
Your capital is at risk.
Significance of Float in Stock Market Dynamics
Why is stock float important in the stock market? A company’s float helps investors understand how many of its shares are available to the public. A company’s floating stock details can show its ownership structure and market position. It also gives investors insights into how it plans to generate revenue during critical times in the stock market.
A company with a limited quantity of trading shares has a low float. The low float stocks are usually more volatile and risky than high-float shares. However, it’s important to note that companies’ floating stocks are not fixed. The floating stock increases when a company sells more shares to the public and decreases when it buys back some of its shares.
Floating is significant in stock market dynamics because it helps companies remain liquid to cover operational expenses for transaction execution. Businesses with high transaction volumes can leverage floating to continuously process transactions without delays or cash flow limitations.
In other words, float stocks are beneficial to both stock companies and investors.
Float and Outstanding Shares Difference
There’s a direct relationship between a company’s float and outstanding shares. These metrics are also crucial to investors because they represent a company’s structure and liquidity.
A company’s outstanding shares represent its stock ownership. It gives a breakdown of its total number of stocks and their holders. These include the firm’s restricted stocks and closely held shares. In other words, if you want to know how many shares a company has issued to investors, you can get the numbers from its outstanding shares.
A company’s stock float is the total number of its shares that public investors can freely buy or sell. A company’s floating stocks are available shares from the outstanding shares after deducting its restricted and closely held stocks.
Information about a company’s outstanding shares, restricted stocks, free float, and closely held shares is usually available in its financial statements. You can find the information directly on the company’s website or leverage the best stock market research and analysis tools.
| Float | A company’s publicly available stocks for trading in the open market without restrictions. |
| Outstanding shares | The total number of stocks a company issues to insiders and public investors. |
Why Float Matters to Investors
Float is vital for stock investors because it affects liquidity and price volatility. A smaller float implies fewer shares available for trading, leading to wider bid-ask spreads and increased price fluctuations. Conversely, a larger float indicates higher liquidity, narrower spreads, and smoother price movements. Understanding float helps investors assess trading conditions and potential risks, such as susceptibility to short squeezes or insider trading. By factoring float into their investment decisions, investors can better navigate the stock market and optimize their portfolios.
What is Float in Stocks? – Formula for Calculating Float
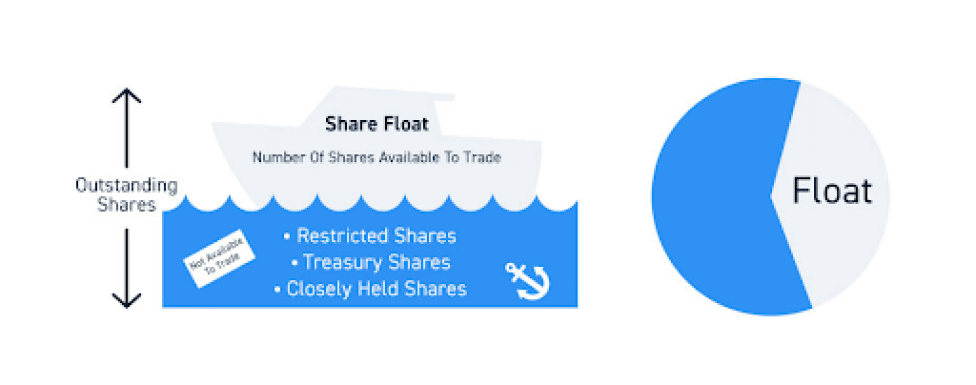
We’ve already established that a company’s outstanding shares do not represent its floating stock value. This is because the outstanding stocks usually contain shares that are not available to the general public for trading.
Apart from restricted and closely owned shares, some companies offer equity stocks to their employees. These also make up its stocks outstanding but won’t contribute to its public float because independent investors cannot buy or sell them.
So, Floating Stock = Outstanding Stock – Restricted Stock – Closely Held Stocks – Employee Stock Options (if available)
For instance, suppose Company A has 10 million outstanding shares but sells 4.5 million shares to institutional investors, offers 1.5 million shares to management, and 1 million to employees.
In that case, the firm’s floating stock will be 10 million shares – 4.5 million shares – 1.5 million shares – 1 million shares = 3 million shares. That means its floating stock percentage is 30% of its outstanding stock.
What is Float in Stocks? – Interpreting Float Percentage

Floating Stock = Outstanding Stock – Restricted Stock – Closely Held Stocks – Employee Stock Options (if available)
After getting the floating stock value, calculating the float percentage is pretty straightforward. The float percentage is the value of the firm’s float compared to its total or outstanding stock.
So, after getting the float, divide it by the outstanding stock to get the float percentage. That is,
Floating Stock Percentage = Float ÷ outstanding shares x 100%
For example, at the time of writing, Amazon had a float of $9.06 billion, and its outstanding shares stood at $10.33 billion. The company’s float percentage is 87.7% ($9.06 billion ÷ $10.33 billion x 100%).
Now that we have answered the question, “What is float in stocks?” you might be looking forward to beginning your float stock trading journey. eToro is our best-recommended stock trading app, with over 30 million users and thousands of tradeable instruments. Follow the steps below to trade stocks on eToro.What is Float in Stocks? – eToro Complete Guide
What is Float in Stocks? – Conclusion
Understanding a company’s stock float is an excellent step in determining its financial health and market value. Float stocks come in low and high forms, but traders prefer companies with larger floats because they are less risky. However, remember to choose a float stock aligned with your investment goals and start trading.
eToro is the number 1 brokerage for investing in float stocks. The online trading platform offers a user-friendly app, low fees, and 4,500+ assets. The top copy trading app also lets you mirror trades from seasoned investors and leverage their trading signals for more potential profits.
Your capital is at risk.
FAQs
What is a good float for a stock?
Is high float good or bad?
Why is low float good?
What is the difference between float and outstanding stock?
Why is float important in stocks?
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Restricted_stock
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Joint-stock_company
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Initial_public_offering
- https://www.fidelity.com/learning-center/trading-investing/fundamental-analysis/understanding-market-capitalization
- https://www.fool.com/terms/s/secondary-market/
- https://smartasset.com/financial-advisor/vesting-period
- https://finance.yahoo.com/quote/AMZN/key-statistics/
- https://www.britannica.com/money/what-is-a-stock-split