What is Zero Knowledge Proof? – Crypto Trading Guide 2026

Blockchain technology has been fully optimized to provide users with high levels of transparency. This development extends to addressing issues such as privacy, security, and safety.
Despite encountering certain flaws, some new cutting-edge protocols have been integrated to counterbalance these challenges. One such protocol is the Zero-knowledge proof, which has proven beneficial to several cryptographic projects.
This guide will answer “What is zero knowledge proof?” and provide illustrative examples.
-
-
Understanding the Concept of Zero Knowledge Proof
There is so much to demystify in cryptocurrency that it may take ample research to understand every concept. However, Zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) is a must-know, as it actively contributes to every process in the financial markets.
So, any investor or trader interested in becoming an expert in cryptocurrency projects should want to know, “What is zero knowledge proof in blockchain?” Understanding this concept will help individuals use cryptocurrencies to their full potential while getting maximum security and privacy.
But before getting into details about ZKPs and highlighting a Zero-knowledge proof example, let’s review the fundamentals of data/information sharing and privacy.
Basics of Information Sharing and Privacy
Businesses, websites, or digital platforms often acquire thousands to millions of personal information from users. However, there is a huge responsibility in how such collected data is handled/managed. Responsible and effective information sharing, with the provider’s consent, offers some benefits.
Conversely, information shared without consent has consequences –misuse and privacy concerns. Third-party organizations may gain access to popular database systems and use it for illicit purposes – often driven by financial motives.
The persistence of this threat inspired blockchain networks to develop a system called Zero Knowledge Proof, where privacy is of utmost priority. This technology will oversee how information data is collected, managed, and shared, ensuring it remains private and secure.
Introduction to Zero Knowledge Proofs in Cryptography
Here is to explain what is zero knowledge proof in crypto.
Zero Knowledge Proof (ZKP) in cryptocurrency is an underlying protocol to determine the accuracy of information or validate a statement without revealing the actual statement. It involves two main entities – the prover and the verifier.
In ZKP, the prover convinces the verifier about the validity of information without disclosing what it is. There won’t be additional information regarding the data – just a validity report. Thus, the former seeks to establish a claim, while the latter accounts for claim verification.
Indeed, Zero Knowledge Proof plays a major role in cryptography, and many paper trading apps have integrated them into their system.
There are two main types, which will be discussed later in the article;
- Interactive Zero Knowledge Proofs, and
- Non-Interactive Knowledge Proofs.
Your capital is at risk.
Importance and Applications
A key takeaway from the ZKP’s description is its pivotal role in maintaining privacy in the blockchain ecosystem. For so long, the cryptocurrency industry relied on personally identifiable information (PII), exposing it to various risks, such as data breaches and cyberattacks.
The traditional method involved sharing data with third-party entities and then stored in central databases. However, the persistent reports of attacks, illegal data sales, and identity theft prompted the need for a more efficient alternative. ZKPs stepped in to address these vulnerabilities.
Below are the significant benefits and applications of Zero Proof Knowledge in blockchain.
Enabling Privacy-Preserving Transactions
So, what is zero knowledge proof in crypto and privacy?
One of the primary functions of ZKPs since its integration into cryptocurrency is to facilitate privacy-preserving transactions. It guarantees that all transactions are carried out securely, safeguarding personal or financial data from exposure.
It assures users that their information remains confidential and protected.
Enhancing Security in Digital Interactions
Similarly, ZKPs play another crucial role in enhancing security in digital processes. This potential results from its privacy-centric function, where information can be verified without disclosing sensitive data. It is a valuable feature in scenarios where sensitive data must remain undisclosed.
For instance, in crypto presales, personal and financial information is acquired for transactions. In this case, ZKPs ensure necessary verification occurs without compromising privacy.
How Zero Knowledge Proof Works
After we’ve discussed “What is zero knowledge proof?” the next part of this article is to explain its operation mechanism.
Fundamental Principles of Zero Knowledge
As mentioned, Zero Knowledge Proof consists of the prover and the verifier. It allows one party to prove knowledge of a statement without disclosing the actual information to the other. This fundamental principle is how the system ensures privacy and eliminates false info.
At its core, it employs a simple verification test. In this test, the prover must prove that the information is correct. If the prover passes, it is valid; failure means false information.
It is synonymous with the two-factor authentication protocol – only that it requires proving an accurate statement.
Zero Knowledge Proofs vs. Traditional Methods
In this article, “What is zero knowledge proof in blockchain?”, we will also discuss how this technique differs from the traditional (PII) method.
Zero Knowledge Proofs Traditional Method - Information verification without revealing data
Information verification with zero privacy - No data storage on servers
Data stored on centralized servers - Minimizes data exposure risk
Vulnerable to cyberattacks - Reduces the need for trust in intermediaries
Information sharing involves third-party. Fig 1: A table showing the differences between Zero knowledge proof (ZKPs) and the traditional method.
Overall, ZKPs are the better approach as the revolutionary protocol allows entities to prove statements with confidentiality. This makes it utilizable within decentralized systems, particularly on blockchain technology networks.
Interactive Zero Knowledge Proofs
Moving on to the different types of ZKPs, the Interactive Zero Knowledge Proof (iZKP) is the most popular. See below for the function and example.
Definition and Functionality
iZKP is a protocol that relies on credible interaction between the two entities involved to ensure the accuracy of an information statement. It involves multiple rounds of communication between the verifier and the prover while upholding privacy.
iZKPs offer excellent flexibility, adaptability, and better efficiency, providing both parties an avenue for communication. This can be leveraged to overcome fraud and other vulnerabilities.
On the other hand, iZKPs lack scalability, so several parties find it difficult to engage in proofs simultaneously. It also increases latency and enhances communication overhead, making conducting a fast and seamless verification impossible.
Example: Schnorr Identification Protocol
Schnorr Identification Protocol is an excellent Interactive zero knowledge proof example. It was named after its creator, Claus Schnorr. This protocol was designed as a public-key-based challenge-response identification protocol to prove knowledge of a discrete logarithm.
In this Schnorr Identification Protocol, two messages are submitted – each with its function. The first message is known as the witness and doesn’t require a secret/challenge value. The second message is a function of the challenge and secret values and the actual witness.
This pre-computed protocol aims to prove ownership of a secret value without disclosing the actual value.
Your capital is at risk.
Non-Interactive Zero Knowledge Proofs
The next popular ZKP is the Non-Interactive Zero Knowledge Proof (niZKP). It is quite different from the former because it allows a prover to generate proof that can be verified. Unlike iZKP, it keeps a single round of communication for maximum efficiency.
Characteristics of Non-Interactive Proofs
Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Arguments of Knowledge (zk-SNARK) is a popular Non-interactive zero knowledge proof example. It mirrors what a non-interactive proof looks like, i.e., using a mathematical algorithm to create a proof without any round of communication.
This cryptographic proof operates on succinctness (relatively small proof size), non-interactivity, and information privacy. It allows generated proofs to be publicly verified with zero communication with the prover. This protocol is faster and doesn’t always have computational complexities.
The limitations of non-interactive proof are its lack of adaptability, potential replay attacks, and specific scalability issues. Because of these problems, they have become technical to use.
Application in Cryptocurrencies: zk-SNARKs
zk-SNARKS gained popularity in blockchain technology due to adopting privacy-focused cryptocurrencies like Zcash. Its non-interactive mechanism of proving ownership of digital assets without revealing the information has been beneficial.
For instance, crypto transaction senders must provide proof of funds using a private key to prove their interest. The plot twist is that this proof of funds does not disclose the amount owned or the wallet addresses.
Interactive zero-knowledge proofs Non-interactive zero-knowledge proofs Multiple rounds of communication Single or no round of communication High computational overhead Simple and practical Uses cryptographic assumptions Relies on Random Oracle Model Fig 2: A table showing the differences between iZKPs and niZKPs
Succinct Zero Knowledge Proofs
Reducing Proof Size with Succinctness
As previously mentioned, one of the characteristics of Succinct Zero Knowledge Proof is its ability to reduce proof size. It performs this through advanced cryptographic methods like algebra, primitives, and compression.
This size reduction with succinctness makes SNARKs suitable for applications where computational resources and space issues persist.
The protocol is opposite to Scalable Transparent Argument of Knowledge (STARK), where larger proof sizes are produced.
Benefits of Blockchain Scalability
One advantage of succinctness in Zero Knowledge proofs is its scalability and application in blockchain networks.
In these networks, space and computational efficiency are paramount; thus, utilizing a specific zero-knowledge proof with minimal size is essential. In that case, zk-SNARKs prove useful. Besides, it is the protocol used in privacy-focused Zcash cryptocurrency trading, to maintain scalability.
Enhancing Privacy in Blockchain Transactions
Role of Zero Knowledge Proofs in Anonymity
The answer to “What is zero knowledge proof in blockchain?” lies in its function.
ZKPs enhance anonymity and privacy in blockchain transactions using an operation mechanism in different aspects, such as transaction validation, credential transactions, address or smart contracts privacy, and scalability. Its integration makes it possible for the user to access data only.
Balancing Transparency and Confidentiality
Unfortunately, blockchain technology faces a serious problem in integrating new systems. One of them is balancing transparency and confidentiality. However, as ZKPs became introduced, they combat these problems and offer more advantages.
Zero-knowledge proofs facilitate transparency on blockchain networks by ensuring compliance with regulatory policies regarding information sharing and against fraudulent activities. Some renowned policies mandated are Anti-money laundering (AML) and Know-your-customer (KYC).
And, of course, its primary role of ensuring privacy means users are guaranteed information confidentiality on the platforms.
Exploring zk-SNARKs in Detail
zk-SNARKs: Zero-Knowledge Succinct Non-Interactive Argument of Knowledge
The Zero knowledge proof example, zk-SNARKS, is a privacy-focused system that enables a prover to convince a verifier that a statement is true without revealing its information. It generates these cryptographic proofs using elliptical curves.
It operates on three core principles – succinctness, zero-knowledge, and non-interactivity.
Typically, it involves three main algorithms;
- Key Generation (Setup): It is the most important stage, and this algorithm generates private or public parameters (key pairs) essential for the system.
- Prover Algorithm: This algorithm takes a proving key as the input. It then generates succinct non-interactive proof of the statement’s validity, sent to the verifier.
- Verifier Algorithm: This algorithm inputs the verification key obtained from the prover to verify proof and the statement’s validity.
Use Cases and Implementations in Cryptocurrencies
Notable use cases and implementations of zk-SNARKs in cryptocurrencies are;
- Identity Verification: zk-SNARKs are used to verify individuals’ identities in a crypto trade. The input key provided by the algorithm to the prover and verifier will help identify fraud and validate transactions.
- Privacy-focused coins: zk-SNARKs have been efficiently used to secure cryptocurrency transactions like Zcash. Since it is a privacy-focused transaction, no specific user details are revealed.
- Smart Contracts and DApps: This cryptographic protocol has been reportedly used in smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) like crypto game apps to ensure integrity and privacy.
- Zk-rollups: The role of zk-SNARKs in ZK-rollups is to ensure scalability and speed. That means numerous transactions, particularly any of the best DeFi projects, can be processed faster.
- Merkle Tree Proof of Reserves: zk-SNARKs has also been used to prove the availability of funds, particularly on major crypto exchanges. For instance, Merkle Tree will allow verifiers to validate a statement provided by a prover with this reserve option.
Your capital is at risk.
Challenges and Limitations
Some challenges and limitations encountered in this cryptographic model include:
Computational Overhead and Verification Complexity
Ideally, zero-knowledge proofs utilize several computational resources. However, this poses significant limitations as provers constantly need to perform complex calculations to generate proofs. It isn’t beginner-friendly, and computational overhead could limit the efficiency of transactions.
Addressing Trusted Setup and Security Concerns
Another problem is solving trusted setup and security concerns. Trust Assumption is a critical element in this protocol, and assessing the participants’ honesty can be difficult.
Either party hopes that the other is honest, which means taking a major risk that could threaten financial security.
Advancements in Zero Knowledge Proof Technology
Even as we have discussed comprehensively “What is zero knowledge proof?” we must highlight significant (future) advancements in this technology. These developments change the system’s general use and solve scalability concerns.
Innovations in Proof Generation and Verification
Established crypto-focused companies are developing ways to improve proof generation and verification processes. They believe it would automatically improve speed and efficiency with transaction requests. That means there will be no long wait times for transaction processing.
Also, the Succinct Non-interactive Arguments (SNARGs) protocol is undergoing new developments to provide succinct arguments without interactive protocols. It would impact several applications.
Potential for Cross-Chain and Interoperable Solutions
zk-SNARKs ushered in cross-chain transaction capabilities with improved privacy. However, while some problems persist, future technological advancements aim to solve this problem, such that users can perform transactions across different blockchain networks without info disclosure.
Broader Applications Beyond Cryptocurrencies
In this “What is zero knowledge proof in crypto?” article section, we will discuss broader applications of this protocol outside the cryptocurrency landscape.
Zero Knowledge Proof in Digital Identity Verification
A real-world application of ZKPs is in digital identity verification processes. Organizations that adopt them will give users autonomy over their sensitive data while strengthening their system’s security and enhancing user privacy.
This ZKP technology allows authentication without revealing their passwords, as opposed to the traditional method of providing one manually. It can also be used to verify digital credentials, such as a university degree, without disclosing included details.
Secure Data Sharing in Sensitive Industries
Sensitive industries like financial institutions and healthcare handle, process, and manage big data that require high-level security and regulatory compliance. However, ZKPs offer a good security measure to help with data management (or data sharing) and prevent cyberattacks or hacks.
Leveraging ZKPs’ strong privacy guarantees will contribute to these sectors’ security-focused reputations for big data.
Balancing Privacy and Regulatory Compliance
Besides “What is zero knowledge proof in blockchain?” balancing privacy and regulatory compliance is also vital. Below are how major ZKP-integrated platforms address regulatory challenges and leverage this technology.
Addressing Regulatory Challenges with Zero Knowledge Proofs
Generally, ZKPs align with regulatory frameworks, and it is only ideal that companies or platforms interested in integrating them into their system meet standards. That would include understanding the landscape, engaging with appropriate authorities, and conducting privacy impact assessments.
ZKP integration requires user consent and transparency. Therefore, as one of the must-dos, these platforms have to communicate and obtain users’ consent regarding data sharing or management.
Navigating Privacy-Enhancing Technologies in a Regulated Environment
As mentioned, Zcash uses the zk-SNARKs protocol, but they encounter limitations due to geo-restrictions. Unfortunately, navigating the landscape of privacy-enhancing technologies in a regulated environment poses serious challenges.
However, cryptographic platforms can meet with regulatory authorities to review compliance requirements for use. If this can be done with both parties reaching a consensus, using zero-knowledge proofs with Zcash and other best altcoins to invest in shouldn’t be a problem.
Your capital is at risk.
Educating and Raising Awareness
Promoting Understanding of Zero Knowledge Proofs
The crypto industry keeps growing, with several users daily. Unfortunately, this evolution brings new technicalities, and it is vital to become updated with the latest information – in this case, the use of zero-knowledge proofs.
Not many cryptocurrency market traders understand what ZKPs can do for them, so platforms must educate and raise awareness after integrating the technology. Users must understand how the cryptographic tool can help them and enhance privacy and security.
Education can be through webinars, seminars, or online course materials.
Encouraging Responsible Use and Development
Similarly, the cryptocurrency market has witnessed cases where individuals have exploited it, often due to negligence, ignorance, or irresponsible use. Platforms must now prioritize encouraging responsible use and development.
Individuals need to know that cryptocurrency investment is good but highly risky. Thus, they must constantly monitor usage and utilize available technologies or features for a seamless transaction experience.
What is Zero Knowledge proof? – eToro Complete Guide
If there is anything gain-worthy from this “What is zero knowledge proof in crypto?” guide, it is how to utilize privacy-enhanced technologies for safety. Some trading platforms have integrated them, and there isn’t any doubt that users will have a good experience.
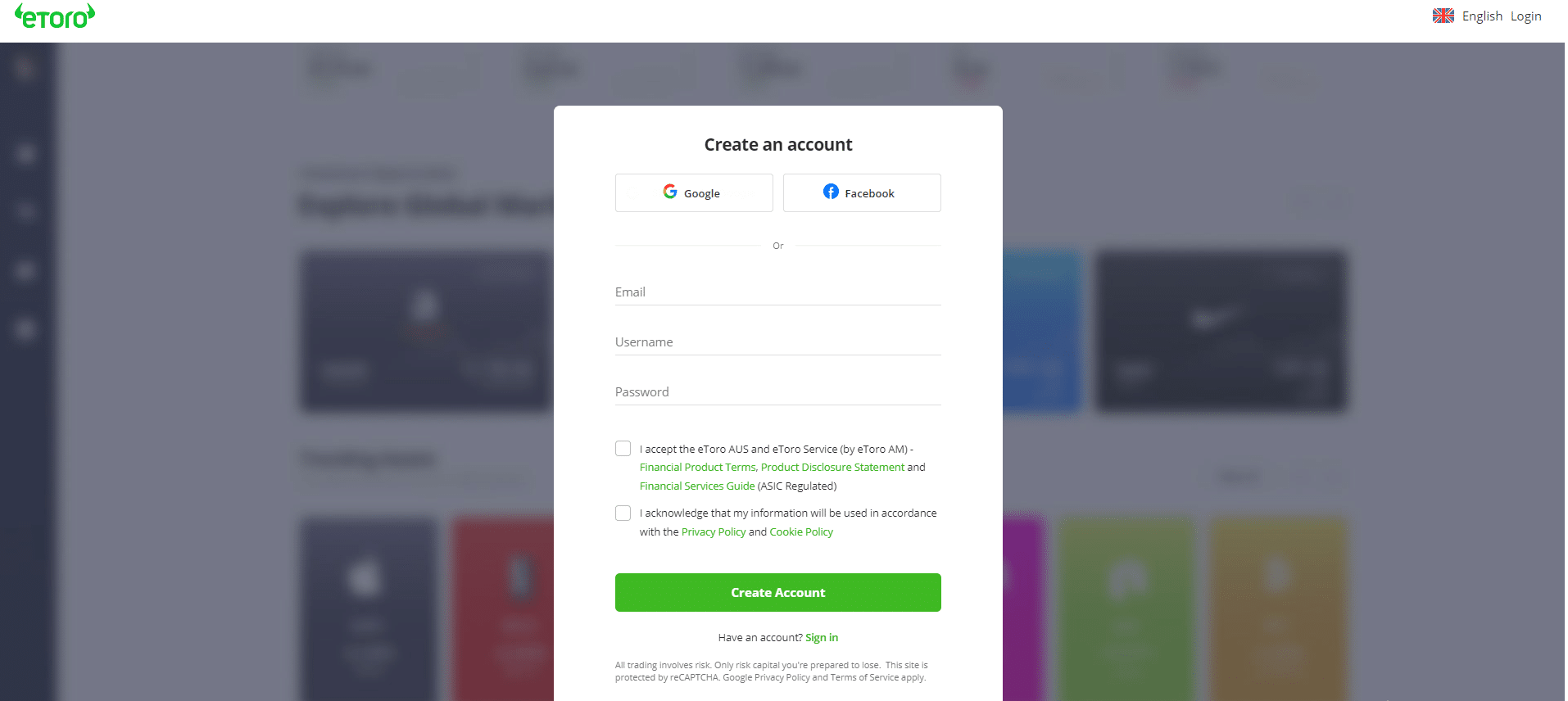
eToro is one of the best crypto and stock trading apps that utilize this technology. It is regulated and allows users to trade effortlessly. Here is a guide on how to open an account on this platform.
Note: Only cryptocurrencies eToro customers in the United States will be able to trade on the platform will be Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, and Ethereum.
Step 1Visit eToro on your smartphone or desktop computer
Step 2Enter requested details, i.e., email address, username, and preferred password.
Step 3Go through the Terms and Conditions and click to accept.
Step 4Click on the “Create Account”
Step 5Proceed to complete further verification processes.
Step 6Deposit funds.
Step 7Start buying or selling cryptocurrencies and meme coins.
Your capital is at risk.
What is Zero Knowledge Proof? – Conclusion
As this article “What is zero knowledge proof?” ends, you must have gained insightful knowledge of ZKPs and their influence in the cryptocurrency market and blockchain landscape. It explores different sections, including the different types, examples, benefits, challenges, and advancements.
With this technology, crypto investors won’t have to worry about privacy or security anymore. We recommend users discover eToro’s potential by creating an account to enjoy privacy-focused, seamless investor trading.
References
- https://www.circularise.com/blogs/zero-knowledge-proofs-explained-in-3-examples
- https://ethereum.org/en/zero-knowledge-proofs/
- https://chain.link/education/zero-knowledge-proof-zkp
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestechcouncil/2023/02/07/what-are-zero-knowledge-proofs/?sh=b80894e6b3e7
- https://hacken.io/discover/zero-knowledge-proof/
FAQs
What is the zero-knowledge proof?
Zero-knowledge proof is a cryptographic protocol that allows a prover validate a statement to a verifier without revealing the content itself.
What is zero-knowledge proof blockchain?
Zero-knowledge proof blockchain is the process of validating a transaction statement on a blockchain network between a prover and a verifier.
What is the difference between proof of knowledge and zero-knowledge proof?
Proof of knowledge is a cryptographic method of demonstrating the truth of a statement and how to arrive that truth by disclosing a specific piece of info. Zero-knowledge proof, on the other, validates a statement without disclosing information.
What is the problem with zero-knowledge proof?
Major problems with ZKPs are computational overhead, trusted setup, scalability, limited applicability, and educational challenges.
Adewunmi Adedayo
View all posts by Adewunmi AdedayoAdewunmi Adedayo is a seasoned finance and cryptocurrency writer with a passion for demystifying financial and crypto concepts to her readers. She has written several content for top websites such as IBtimes UK and The Nigerian Tribune. Adewunmi's style entails transforming technical topics into simple, captivating, and concise content for her audience.
VISIT ETOROYour capital is at risk. Other fees apply. For more information, visit etoro.com/trading/fees.stockapps.com has no intention that any of the information it provides is used for illegal purposes. It is your own personal responsibility to make sure that all age and other relevant requirements are adhered to before registering with a trading, investing or betting operator. Contracts for Difference (“CFDs”) are leveraged products and carry a significant risk of loss to your capital. Please ensure you fully understand the risks and seek independent advice.By continuing to use this website you agree to our terms and conditions and privacy policy.
Trading is risky and you might lose part, or all your capital invested. Information provided is for informational and educational purposes only and does not represent any type of financial advice and/or investment recommendation.
Crypto promotions on this site do not comply with the UK Financial Promotions Regime and is not intended for UK consumers.
© stockapps.com All Rights Reserved 2026