Bitcoin(BTC) may be an incredible innovation in currency and finance. It has revolutionized our financial landscape, changing our thinking about funds transfers and investments. But, as with any new technology, it has its drawbacks. BTC has a significant e-waste problem.
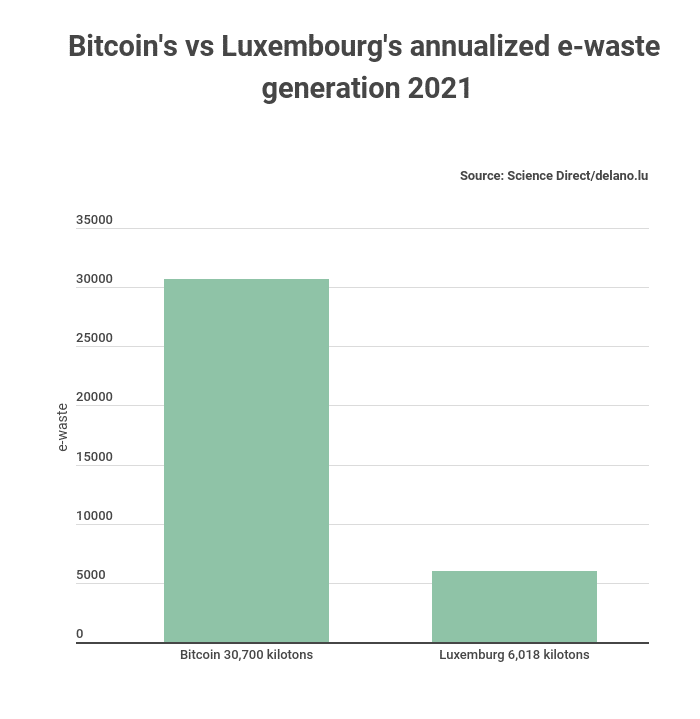
BTC’s annual e-waste exceeds the total e-waste that some countries generate. According to a StockApps.com analysis, BTC’s annual e-waste generation amounts to 30, 700 metric tons. This amount of e-waste is five times the total generated by Luxembourg (roughly 6 kilotons).
“The fact that Bitcoin mining produces 30.7 kilotons of waste annually is worrying,” says StockApps’ Edith Reads. She adds, “Today, BTC mining generates over five times the amount that Luxembourg does. That’s a pretty staggering figure, especially when you consider that Luxembourg has a population of only 600,000 people.”
Why is BTC mining a “dirty” venture
Bitcoin’s environmental issues stem from its architecture. The King Crypto uses a proof of work (PoW) mining consensus mechanism that is both energy and hardware intensive. Cambridge Bitcoin Electricity Consumption Index estimates that BTC uses roughly 119 TWh annually. That’s nearly 25 times Luxembourg’s annual consumption (7.54 TWh).
That amount of energy consumption comes with its downsides; the frequent wear and tear of the coin’s mining equipment. In the beginning, it was profitable to mine BTC using regular PCs. But the crypto’s mining difficulty grows with time, necessitating the use of advanced miners the application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs).
ASICs are tailor-made for mining, but they have short life spans. An average ASIC is profitable for roughly 18 months, after which they tend to become obsolete. Miners, therefore, have to acquire new ones leading to some sort of arms race for computational power. That has created an accumulation of decommissioned ASICs adding to the earth’s environmental woes.
What would it take to reverse BTC’s e-waste problem?
Mitigating Bitcoin’s e-waste footprint requires concerted efforts from the coin’s enthusiasts. A significant part of those efforts should concentrate on reducing its energy and hardware demands. That entails migrating from the current PoW consensus mechanism to an environmentally sound one.
For example, Crypto analysts have suggested a movement to the Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. PoS uses significantly lesser energy resources than PoW; it also doesn’t require sophisticated hardware for profitable mining. Adopting such a consensus mechanism will substantially cut down the number of devices that BTC mining renders obsolete yearly.
Another suggestion has been for BTC to adopt a pre-mining mechanism akin to XRP. Instead of mining new coins, the system algorithmically produces them and releases them in bits. Such a system will still depend on decentralized verification but cuts down on the need for high-tech mining equipment.

Question & Answers (0)